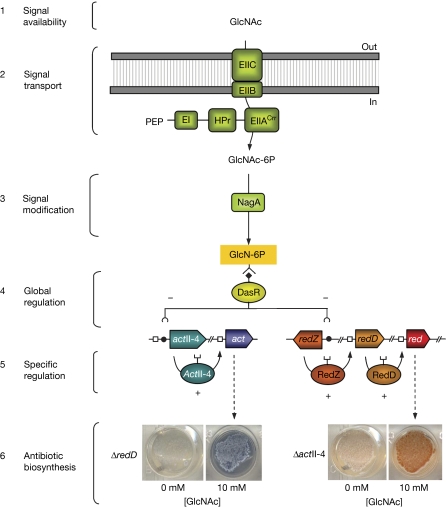
Figure 4.
Model of GlcNAc-dependent signalling in streptomycetes. GlcNAc enters the cytoplasm and is phosphorylated by the PTS, which is composed of intracellular general PTS proteins EI, HPr and EIIA, and the GlcNAc-specific EIIB and EIIC components. N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate (GlcNAc-6P) is deacetylated by NagA. The resulting glucosamine-6-phosphate (GlcN-6P) is an allosteric effecter of DasR that inhibits its DNA binding, resulting in the loss of transcriptional repression of actII-ORF4 and redZ, and thereby activating actinorhodin (Act) and undecylprodigiosin (Red) production, respectively. The stimulatory effect of GlcNAc on antibiotic production is visualized by using the S. coelicolor mutants M511 (Act non-producer) and M510 (Red non-producer), respectively. E, enzyme; GlcNAc, N-acetylglucosamine; NagA, N-acetylglucosamine deacetylase; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PTS, phosphotransferase system.