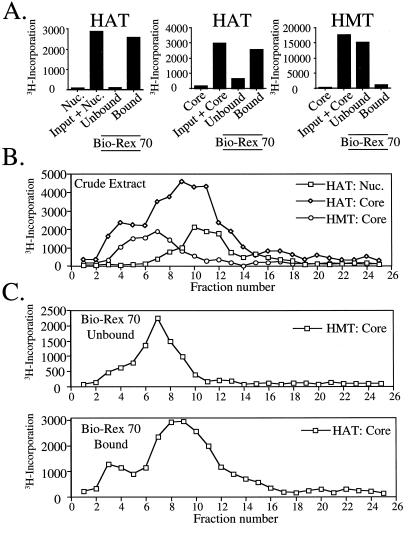
Figure 2.
Macronuclear HAT and HMT activities are physically separable. (A) DNase I extracts prepared from Tetrahymena macronuclei were incubated with the resin Bio-Rex 70 and bound proteins were eluted with 0.8 M NaCl before analysis of either HAT or HMT activity of the unbound or bound fractions by filter-binding assays using chicken core histones (Core) or nucleosomes (Nuc.) as substrate. The first two bars in each panel depict control experiments showing substrate only or substrate plus macronuclear extract (input) before the binding analysis. (B) Macronuclear extracts were fractionated by using a Superose 12 size exclusion column and collected fractions were analyzed for HMT and HAT activities by filter-binding assays as in A. (C) Bound- and unbound-Bio-Rex 70 fractions from DNase I extracts (see A) were fractionated by using Superose 12 and analyzed for free histone HAT and HMT activity. As only background levels of HAT and HMT activity were detected in the unbound- and bound-Bio-Rex 70 fractions, respectively, these data were omitted for clarity.