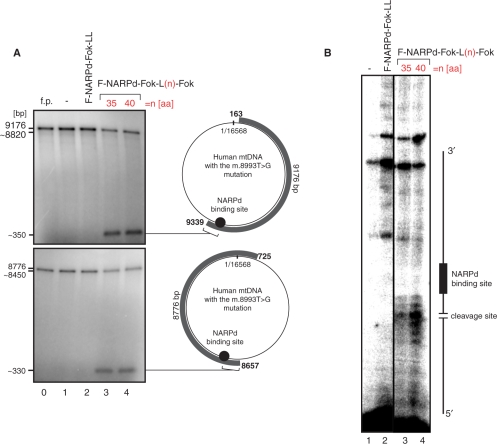
Figure 3.
The specificity of single-chain ZFNs designed to target the mitochondrial point mutation. (A) In vitro assay verifying the specificity of the F-NARPd-Fok-L35-Fok (line 3) and F-NARPd-Fok-L40-Fok (line 4) constructs to a single site in human mtDNA. The assay was performed similarly to the experiment shown in Figure 2. The DNA probes used here though were generated in a long-range PCR reaction so that the two resulting products represented the entire mtDNA molecule harbouring the m.8993T>G substitution (grey curved bars with the mtDNA coordinates given on each end). The PCR products were radioactively labelled using T4 Kinase. (B) Mapping the main cleavage sites of F-NARPd-Fok-L35-Fok and F-NARPd-Fok-L40-Fok constructs by primer extension. Unlabelled DNA probes (as described above) were subjected to the in vitro digestion assay with F-NARPd-Fok-L35-Fok (line 3) or F-NARPd-Fok-L40-Fok (line 4). Next the digested DNA served as a template for the extension reaction of the 5' labelled primer that anneals 100-bp upstream from the NARPd-binding site. DNA strand breaks introduced by F-NARPd-Fok-L35-Fok or F-NARPd-Fok-L40-Fok map to several sites 2–7-bp upstream from the NARPd-binding site.