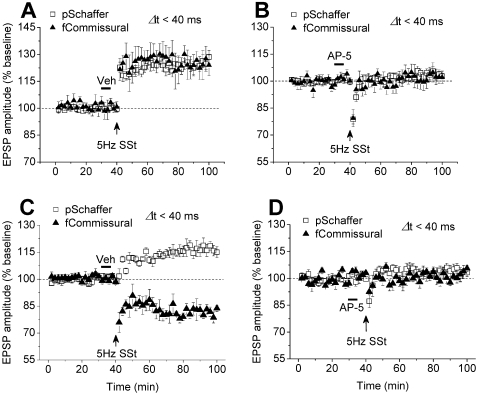
Figure 4. The activity-dependent synaptic plasticity depends on NMDAR.
A, Intracerebroventricular infusion of vehicle did not prevent the stimulation to Schaffer preceding commissural pathway (Δt<40 ms) from inducing LTP in both pathways in pentobarbital-anesthetized rats (n = 5; Schaffer: 125.7±3.2%; commissural: 123.9±6.2%; P<0.001 vs. baseline of Schaffer or commissural). B, Infusion of the NMDAR antagonist AP-5 prevented the stimulation to Schaffer preceding to commissural pathway within a 40-ms window from inducing LTP in both pathways (n = 6; Schaffer: 103.6±2.2%, P = 0.349 vs. baseline; commissural: 103.0±4.1%, P = 0.463 vs. baseline). C, Similarly, infusion of vehicle did not affect the stimulation to Schaffer preceding to commissural pathway within a 40-ms window to induce LTP in preceding and LTD in following pathway in urethane-anesthetized rats (n = 6; Schaffer, 116.8±3.2%; commissural, 81.4±2.3%, P<0.001 vs. baseline of pSchaffer or fcommissural). D, Infusion of the NMDAR antagonist AP-5 prevented the stimulation to Schaffer preceding to commissural pathway within a 40-ms window from inducing LTP and LTD (n = 4; Schaffer: 103.8±2.9%, P = 0.163 vs. baseline; commissural: 102.6±2.4%, P = 0.493 vs. baseline).