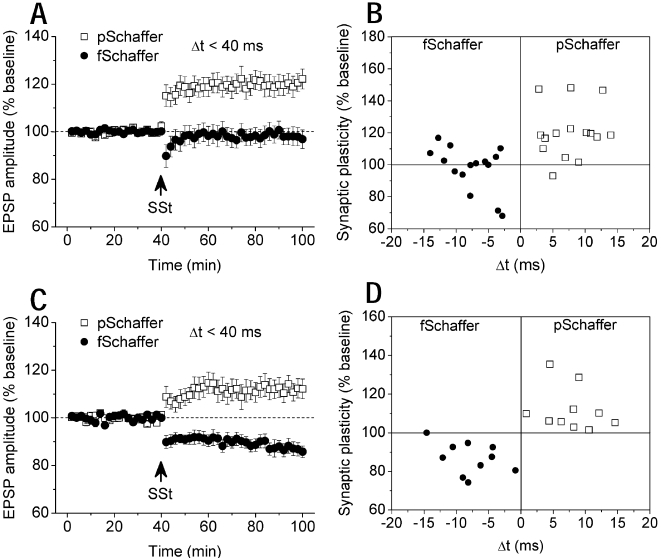
Figure 5. Coincident activity of Schaffer pathways enables synaptic plasticity in CA3-CA1 network.
A, In pentobarbital-anesthetized rats, SSt to two Schaffer pathways with one preceding the other (Δt<40 ms) induced LTP in the pSchaffer without affecting synaptic efficacy in the fSchaffer pathway (n = 15; pSchaffer: 120.3±4.0%, P<0.001 vs. baseline; fSchaffer: 97.8±3.5%; P = 0.273 vs. baseline; P<0.001 pSchaffer vs. fSchaffer). p = preceding; f = following. B, Individual data confirmed this finding for activity-dependent LTP. C, In urethane-anesthetized rats, SSt to two Schaffer pathways within a 40-ms window consistently induced LTP in the preceding and LTD in the following pathway (n = 10; pSchaffer: 112.0±3.6%, P = 0.007 vs. baseline; fSchaffer: 86.6±2.6%; P<0.001 vs. baseline). D, Individual data confirmed consistent LTP and LTD in the pSchaffer and fSchaffer pathway, respectively.