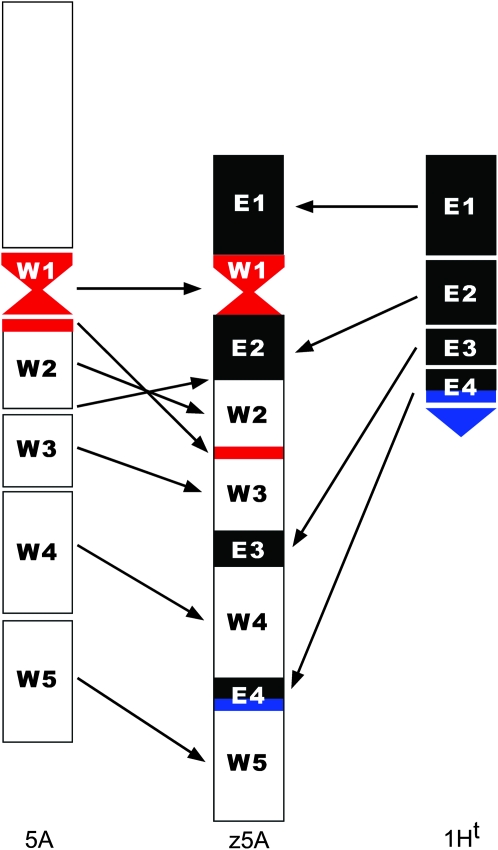
Figure 3.—
Proposed origin of chromosome z5A by chromosome breakage and fusion of the broken chromatin blocks. (Left) Wheat chromosome 5A, (middle) z5A, and (right) telosome 1HtS, from which the four Elymus segments present in z5A were derived. The centromeres of wheat and Elymus are shown in red and blue, respectively. The original centromere of wheat chromosome 5A was split into two portions in z5A. The major part is the functional centromere, located within the W1 segment, and the smaller part is located in W2. The third and smallest centromere was derived from part of the centromere of chromosome 1Ht (E4). Marker analysis indicated that the entire short arm of 1Ht was not present in z5A. GISH and meiotic pairing analyses showed that the E1 segment was derived from the distal region of 1HtS and W4 was derived from the distal region of 5AL. Because the marker order in segments E1 and E4 is conserved relative to wheat, but reversed in segments E2 and E3, either a paracentric inversion in the short arm preexisted in 1Ht or fusion of the broken chromatin blocks occurred, as indicated.