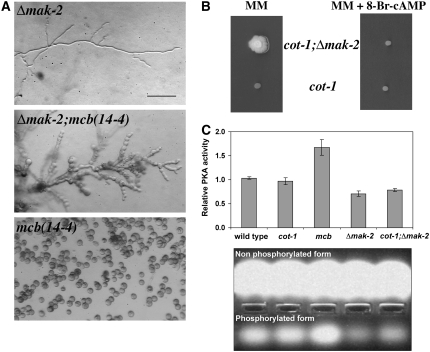
Figure 2.—
PKA activity is reduced in Δmak-2. (A) Morphology of Δmak-2; mcb(14-4) and mcb(14-4);Δmak-2 germinated for 12 hr at 37°. Bar, 20 μm. (B) Growth of cot-1(ts) and cot-1(ts);Δmak-2 on minimal media and media supplemented with 500 μm 8-Br-cAMP at restrictive temerature. (C) PKA activity in extracts of germinating conidia of wild type, cot-1(ts), mcb(14-4), Δmak-2, and cot-1(ts);Δmak-2, 11 hr post-inoculation, relative to wild type. Cultures were incubated in prewarmed liquid Vogel's minimal medium at 36° and were assayed for PKA activity. Data presented in the graph are means of at least four independent experiments with two replicates each. Standard errors are shown. (Bottom) A selected experiment demonstrating the nonphosphorylated and phosphorylated (indicating PKA activity) fluorescent Kemptide substrates, migrated to the anode and cathode of the agarose gel, respectively. The PepTag assays utilize fluorescent peptide substrates specific for PKA. Phosphorylation of the substrate by PKA alters the peptide's net charge from +1 to −1, allowing separation of the phosphorylated substrate from the nonphosphorylated on the agarose gel.