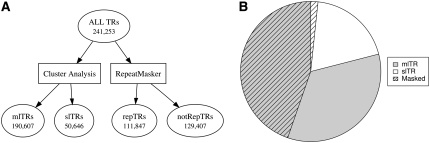
Figure 1.—
Classification of human tandem repeats. (A) Steps taken to produce two paired subsets of tandemly repeated sequences in the human genome sequence. Numbers indicate the number of tandem repeats in each subset. The 241,653 entries in the ALL TRs set were chosen from the complete list of tandem repeats in TRDB by selecting only those with periods between 20 and 2000 bp and removing entries redundant by identical genome locations. slTRs or “single-locus tandem repeats” possess consensus sequences found only once in the human genome while the consensus sequences for mlTRs or “multilocus tandem repeats” are related to sequences elsewhere in the genome. repTRs are tandem repeats whose consensus sequence is “masked” by RepeatMasker due to similarity to known human repetitive elements; notRepTRs represent the remaining tandem repeats unmasked by RepeatMasker. (B) Pie chart showing the composition of the ALL TRs by comparing the two pairs of subsets, mlTRs and slTRs vs. repTRs and notRepTRs. The hatched overlay depicts the fraction of ALL TRs masked by RepeatMasker.