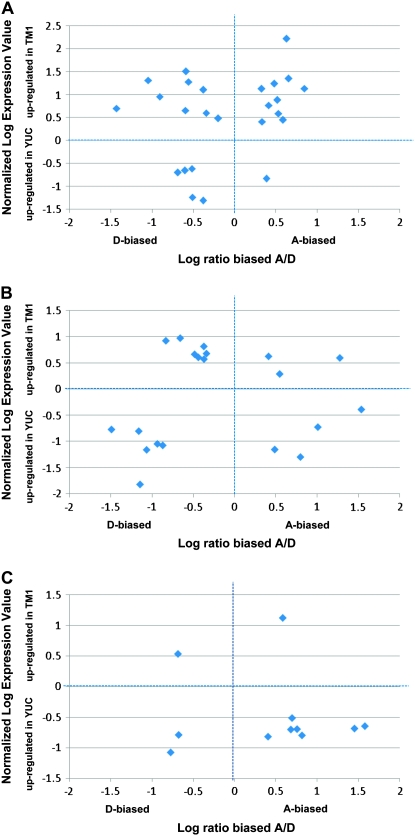
Figure 3.—
Gene recruitment during G. hirsutum domestication. In addition to homeolog-specific probes, the microarray platform contains “generic” probes targeting both homeologs. Thus, this microarray platform interrogates both homeolog-specific and total (duplicate) gene expression. Significant differences in gene expression during domestication were determinate as previously described (Hovav et al. 2008a). Shown are the relationships between homeolog-specific expression ratios, using only genes that changed both in bias (x-axis) and in total expression (y-axis) during domestication, using q-values of FDR < 0.05 as the threshold. A, B, and C are for 5, 10, and 20 DPA, respectively. Genes upregulated in the domesticated form (top) can be considered as candidates for D genome (left) or A genome (right) recruited during G. hirsutum domestication. The list of genes and their putative biological roles are shown in supplemental Table 1.