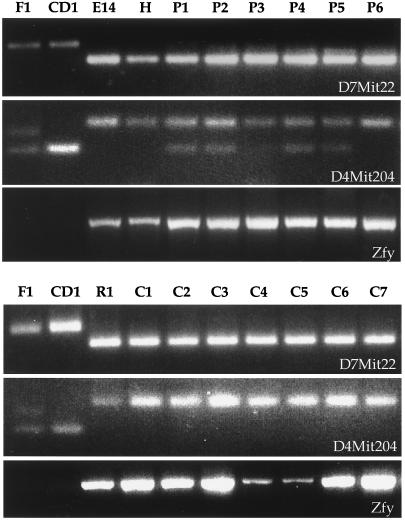
Figure 4.
DNA genotyping corroborates the ES cell provenance of Hooper and other cloned mice. Results for polymorphic DNA markers on chromosome 7 (D7Mit22) and chromosome 4 (D4Mit204) are shown. Confirmation of sex was with PCR primers for the Y-chromosome specific Zfy gene (Zfy). The oocyte donor strain is B6D2F1 (F1), and female surrogates used to carry the pregnancies are of a CD-1 background. (Upper) E14 derived clones. Genomic DNA was from placentae for cloned offspring P1–P6. Genomic DNA from an ear-punch biopsy of Hooper is indicated by H. The weak lower band for the D4Mit204 marker is shared between the placental samples of cloned offspring and the CD-1 sample in a manner consistent with the expected presence of both CD-1-derived (maternal) and clone-derived (E14) cells in the placenta. Accordingly, this lower band is absent from the ear-punch biopsy DNA sample of Hooper (H), whereas it is present in the corresponding placental DNA sample (P1). (Lower) R1-derived clones. Genomic DNA was from tail biopsies for cloned offspring C1–C7.