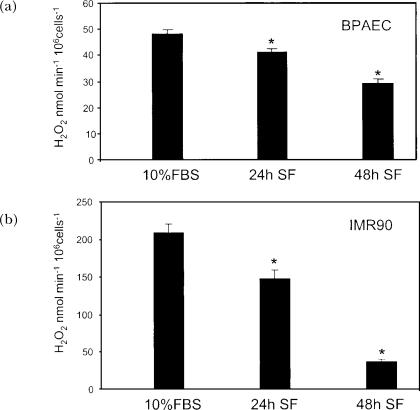
FIGURE 2.
Effect of growth arrest on endogenous production of extracellular H2O2 by bovine PAEC and IMR90. Bovine PAEC (BPAEC) (A) or IMR90 human lung fibroblasts (B) were subcultured at 4×104 cells/35 mm dish in RPMI supplemented with 10% FBS. 24 h and 48 h after plating, medium was replaced with serum free (SF) RPMI. Extracellular H2O2 was determined as described previously (Thannickal et al., 1993), and normalized to cell numbers. Briefly, cells were washed with Hanks' buffered saline, without phenol red, pH 7.4. Cells were then placed in Hanks saline containing 1mM HEPES, 100 μM homovanillic acid, 5 units/ml horseradish peroxidase, type IV. The conditioned medium was collected after 1 h, and the pH was adjusted to 10.0 with 0.1 M glycine-NaOH buffer. Fluorescence was measured at excitation and emission wavelengths of 321nm and 421nm, respectively. Control samples were made containing the reaction mixture alone, and incubated in the absence of cells to correct for spontaneous dimerization of homovanillic acid. A standard curve was generated using known concentrations of H2O2 incubated with the reaction solution. Values represent means ± SD, n=3. ∗Values differ from 10% FBS at p<0.05.