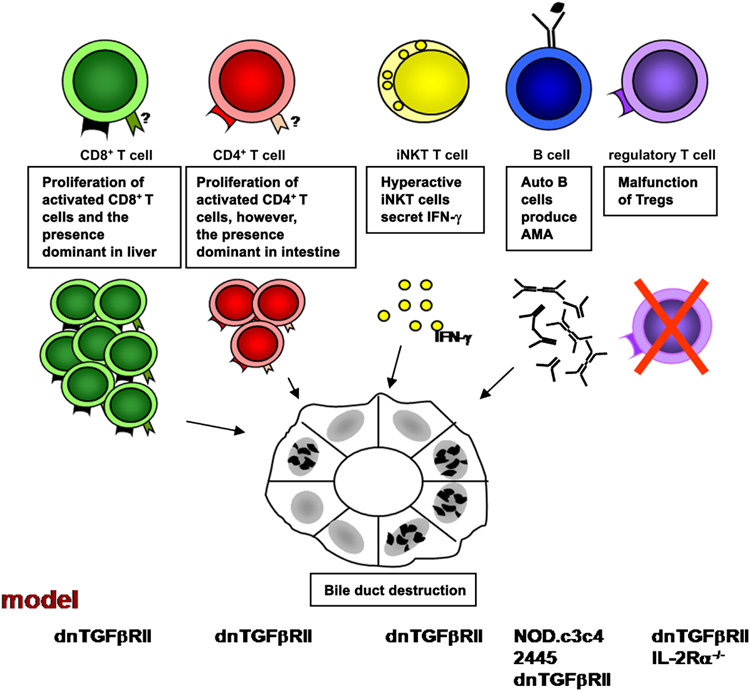
Figure 2.
Immune cells are involved in the early pathogenesis of PBC. T cells mediating the destruction of bile duct in PBC is documented in the dnTGFβRII model by adoptive transfer study. Rag-1−/− mice transferred with CD8+ T cells from dnTGFβRII mice demonstrate a significant expansion of T cells and the presence of portal tract infiltrate. However, the specific homing receptors for CD4+ and CD8+ T cells have not been identified. iNKT cells promote the development of PBC in early stages by secreting IFN-γ. Anti-PDC-E2 autoantibodes are detected in NOD.c3c4, 2445, dnTGFβRII, and IL-2Rα−/− mouse models. The presence of liver disease similar to human PBC in dnTGFβRII and IL-2Rα−/− mouse models indicates the importance of Tregs in PBC.