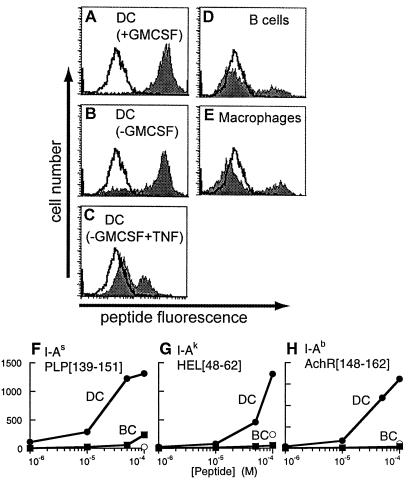
Figure 5.
Peptide binding by empty cell-surface class II MHC molecules. (A–E) Peptide binding to cell-surface IAs on bone marrow-derived DC in various developmental states (A–C), B-cell blasts (D), or macrophages (E), by using 100 μM fluorescent antigenic peptide PLP[139–151] (shaded) or control peptide PLP[39–50] (unshaded), detected by flow cytometry. Proportion of cells staining positive for surface peptide binding: DC (+GM-CSF) 99%, mature DC (−GM-CSF) 81%, DC (−GM-CSF, +TNF) 29%, macrophages 23%, B-cell blasts 21%. (F–H) Concentration dependence of antigenic peptide binding to splenic DC (filled circles) and B-cell blasts (filled squares) and of control peptide binding to splenic DC (open circles). (F) PLP[139–151] binding to DC and B cells from SJL (IAs) mice with nonbinding control peptide PLP[39–50], (G) HEL[48–62] binding to B10.Br (IAk) cells with control peptide OVA[323–336], and (H) AchR[148–162] binding to C57/Bl6 (IAb) cells with control peptide MBP[1–11].