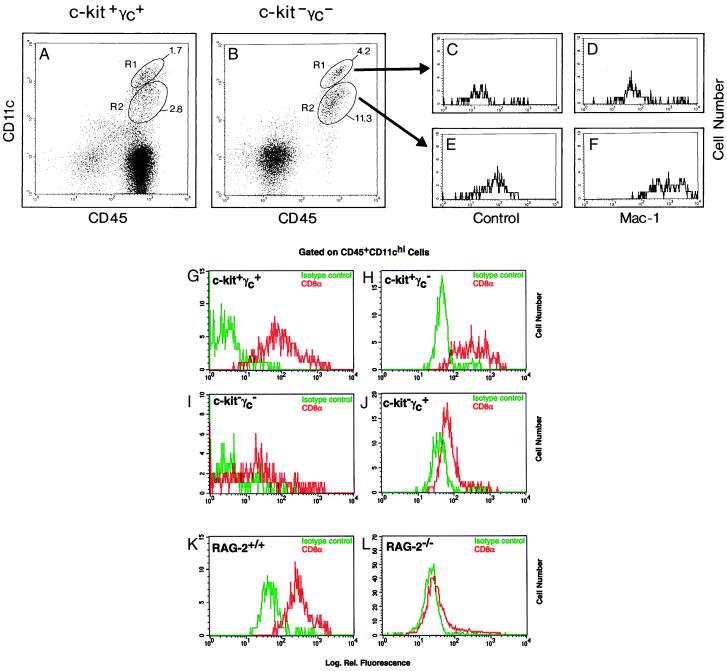
Figure 5.
Both myeloid and lymphoid DC phenotypes (see text) are generated in the absence of pro-thymocytes. Wild-type (A, G, and K), c-kit−γc− (B–F and I), c-kit+γc− (H), c-kit−γc+ (J), RAG-2+/+ (K), and RAG-2−/− (L) mice were analyzed for expression of CD45 and CD11c (A and B), or CD45, CD11c and Mac-1 (B–F), or CD45, CD11c, and CD8α (G–L). CD45+CD11c+ DC can be separated into CD11chigh and CD11clow populations (A and B) which, purified by cell sorting, were restained with isotype controls (C and E) or with anti-Mac-1 (D and F). CD11chigh DC are Mac-1−/low [mean fluorescences are 38 (C) vs. 201 (D)], whereas CD11clow DCs are Mac-1+ [mean fluorescences are 88 (E) vs. 1297 (F)]. CD8α expression on CD11chigh DCs was compared between wild-type (G), c-kit+γc− (H), c-kit−γc+ (J), and c-kit−γc− (I) mice and between RAG-2+/+ (K) vs. RAG-2−/− (L) mice (isotype control in green; CD8α staining in red). CD8α expression was negative/low in DCs from c-kit−γc− thymi and from RAG-2−/− thymi when compared with DCs from wild-type thymi. Mean fluorescences and peak channels were 5 and 1 [isotype (G)], 163 and 63 [anti-CD8α (G)]; 57 and 46 [isotype (H)], 445 and 289 [anti-CD8α (H)]; 9 and 1 [isotype control (I)], 67 and 1 [anti-CD8α (I)], 48 and 31 [isotype control (J)], 84 and 64 [anti-CD8α (J)], 57 and 39 [isotype control (K)]; 355 and 228 [anti-CD8α (K)]; 23 and 19 [isotype control (L)], and 51 and 23 [anti-CD8α (L)].