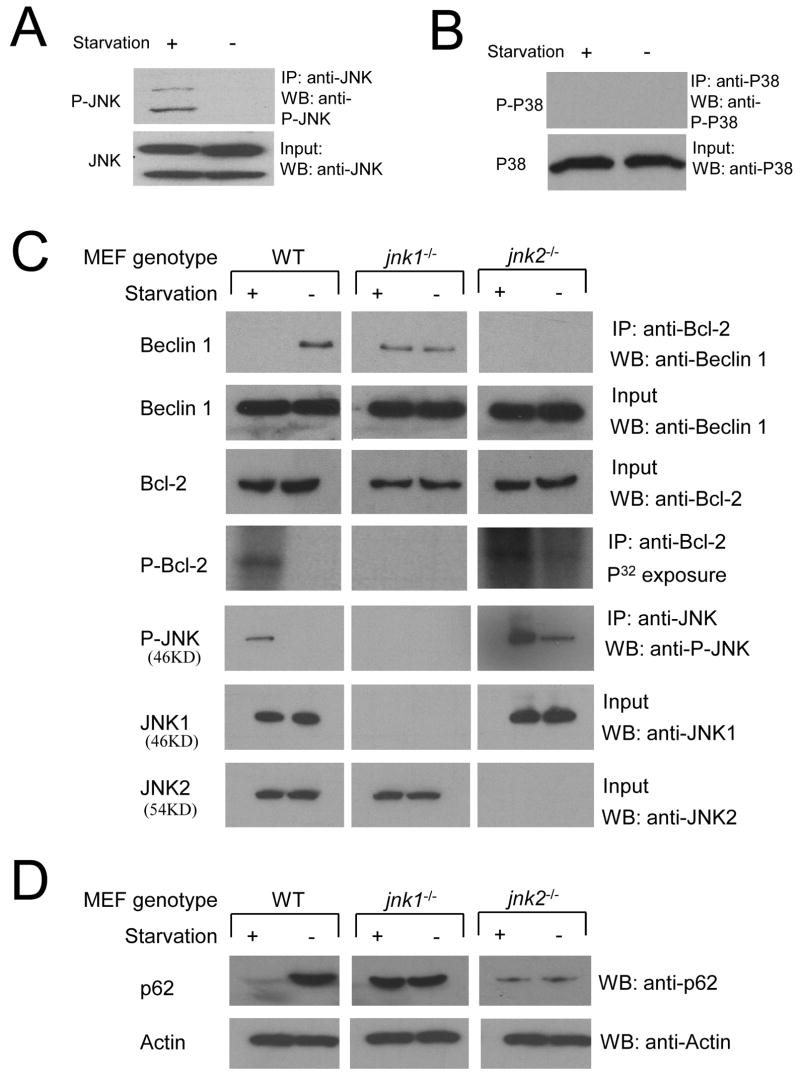
Figure 5. Endogenous jnk1 is Required for Starvation-Induced Bcl-2 Phosphorylation, Dissociation of the Bcl-2/Beclin 1 Complex, and Autophagy.
(A and B) Western blot analysis of active JNK (A) and active P38 (B) in MCF7.beclin 1 cells grown in normal media (starvation -) or in HBSS for four hours (starvation +), Active JNK was detected by immunoprecipitation using a polyclonal goat anti-JNK antibody, followed by Western blot analysis with a rabbit polyclonal Thr183/Tyr185 phosphorylation specific JNK antibody (A, upper panel). Active P38 was detected by a rabbit polyclonal phospho-P38 MAP kinase (Thr180/Tyr182) antibody (B, upper panel). Total JNK and P38 (A–B, lower panels) were detected by rabbit polyclonal JNK and p38 MAP kinase antibody, respectively.
(C) Comparison of Beclin 1 co-immunoprecipitation with Bcl-2 (top panel), Bcl-2 phosphorylation (fourth panel) and JNK phosphorylation (fifth panel) in wild-type (WT), jnk1−/− and jnk2−/− MEFS during growth in normal media (starvation -) or in HBSS for four hours (starvation +). Other panels represent the total amount of Beclin 1 (second panel), Bcl-2 (third panel), JNK1 (sixth panel) and JNK2 (bottom panel) detected in cell lysates by Western blot analysis with the indicated antibody.
(D) Comparison of p62/SQSTM1 levels in WT, jnk1−/− and jnk2−/− MEFS during growth in normal media (starvation -) or in HBSS for four hours (starvation +). Actin is shown as a loading control.