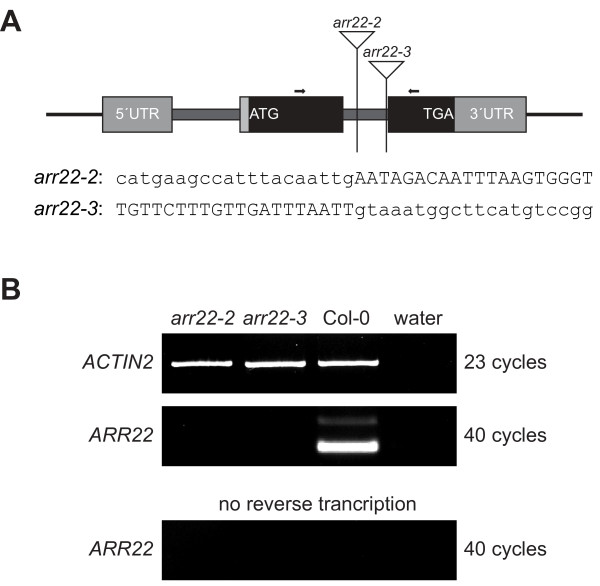
Figure 5.
Characterization of ARR22 T-DNA insertion mutants. (A) Scheme of the ARR22 (At3g04280) locus and positions of T-DNA insertions. The exons are depicted as filled boxes (coding region in black, UTR in grey), introns as thick lines, and the T-DNA insertions as triangles. The sequences at the insertion of the T-DNA (lower case letters) into the Arabidopsis genome (upper case letters) are given for both alleles (arr22-2, arr22-3). Arrows indicate the sites of primers used for RT-PCR analysis. (B) End-point RT-PCR analysis of the steady-state level of ARR22 transcript. The cDNA was derived from total RNA extracted from siliques of the two allelic homozygous arr22 T-DNA insertion lines (arr22-1, arr22-2) and wild type (Col-0). PCR was perfomed with the ARR22-specific primers indicated in (a) and, as a control, with ACTIN2-specific primers. To exclude any cross-contamination and contamination with genomic DNA, the RT-PCR was performed in the absence of total RNA or without its reverse transcription.