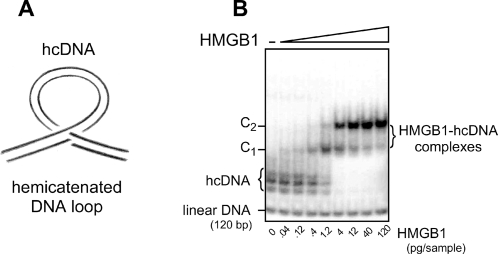
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic representation of a hemicatenated DNA loop (hcDNA). A double-stranded DNA fragment is folded into a loop maintained at its base by a hemicatenane, i.e. the junction of two double-stranded DNA molecules in which one of the strands of one duplex passes between the two strands of the other duplex, and reciprocally. (B) Gel electrophoresis of hcDNA and its complexes with HMGB1. A 120 bp DNA fragment was 32P end-labeled and used to prepare hcDNA, which was analyzed by electrophoresis on a 4% polyacrylamide gel. hcDNA (left lane) migrates as several bands as a function of the size and of the location of the loop along the structure. Addition of the indicated amounts of pure HMGB1 results in the formation of DNA-protein complexes that migrate as two retarded bands, C1 and C2, corresponding to the binding of one or two HMGB1 molecules per hemicatenane, respectively. For the low protein concentrations the amount of shifted hcDNA is proportional to the protein amount, with a lower detection limit of 0.04 pg HMGB1 [21]. At high protein concentrations, when all the hcDNA probe is complexed with HMGB1, the amount of hcDNA becomes limiting and further addition of HMGB1 does not modify the band pattern.