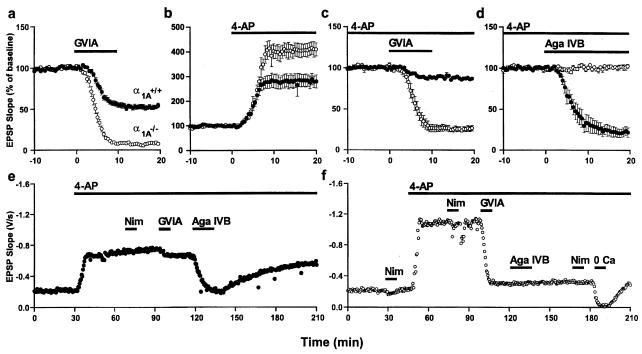
Figure 5.
Effects on synaptic transmission of altering Ca2+ influx in wt (●) and mutant (○) animals. (a) Blockade of N-type Ca2+ channels with ω-CTx-GVIA (1 μM) reduced the strength of synaptic transmission by half in wt but eliminated the EPSP in mutants. (b) Enhancement of Ca2+ influx by broadening action potentials with 4-AP (100 μM) increased the strength of synaptic transmission by 2-fold in wt and 3-fold in mutants. (c) After application of 4-AP, blockade of N-type Ca2+ channels considerably reduced synaptic strength in α1A−/− slices, with a much smaller effect in wt slices. (d) After application of 4-AP and ω-CTx-GVIA, blockade of P/Q-type Ca2+ channels with ω-Aga-IVB (1 μM) decreased the strength of synaptic transmission in wt by more than three-quarters but had no effect in mutants. (e and f) Representative responses to sequential application of Ca2+ channel blockers in the presence of 4-AP in wt (e) and α1A−/− (f) animals.