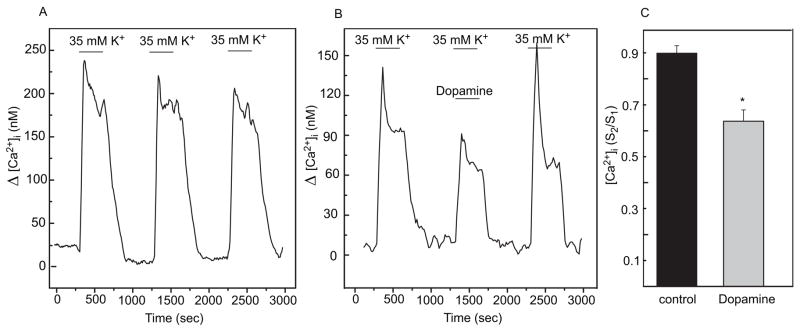
Fig. 2.
Dopamine inhibits the depolarization-evoked increase in [Ca2+]i in cultured chicken photoreceptor cells. A. Representative trace of [Ca2+]i recording of identified photoreceptor cells treated with three repetitive stimulations with 35 mM KCl. K+-evoked depolarizations produce highly reproducible increases in [Ca2+]i. B. Representative trace of [Ca2+]i recording of identified photoreceptor cells treated with three repetitive stimulations with 35 mM KCl and dopamine (0.1 μM) added during the 2nd stimulation (S2). C. Plots of S2/S1 ratios (S2 = peak area during the 2nd stimulation, and S1 = peak area during the 1st stimulation); n= 12 for controls; n=8 for dopamine; * p<0.05 vs control.