Table 5.
Model fitting results for an interaction model of full scale IQ with mean real estate price as moderator
| Mean real estate price | −2LL | Df |
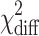
|
Dfdiff | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Full model | 5588.163 | 723 | |||
| 1a | Equalize unmoderated parts of variance (a, c, an e) across sex and cohort | 5602.742 | 732 | 14.579 | 9 | 0.10 |
| 1b | Equalize unmoderated part means (m) across sex and cohort | 5607.506 | 735 | 4.764 | 3 | 0.19 |
| 1c | Drop parameter c | 5607.507 | 736 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.97 |
| Model 2 | Equalize moderation parameters a′, c′ and e′ (variances) across sex and cohort | 5611.287 | 745 | 3.781 | 9 | 0.93 |
| Model 3 | Drop all moderation on the variances | 5616.798 | 748 | 5.511 | 3 | 0.14 |
| Model 3a | Drop all but moderation in E of older males (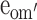 ) ) |
5611.774 | 747 | 5.024 | 1 | <0.05 |
| Model 4 | Equalize moderation parameter means (m′) across sex and cohort | 5613.055 | 750 | 1.281 | 3 | 0.73 |
| Model 5 | Drop moderation means | 5616.713 | 751 | 3.658 | 1 | 0.06 |
| Parameters final model | ||||||
| Means | m = 103.7412 | Variances | A = 10.4655 | |||
| m′ = 0.38 | E = 4.8456 | |||||
| e′om = 0.4649 | ||||||
Note: Parameters a, c and e refer to the unmoderated parts of the variance components A (additive genetic effects), C (common environmental effects) and E (unique environmental effects) of FSIQ, while parameters a′, c′ and e′ refer to the moderation parameters of these variance components. Parameter m refers to the unmoderated part of the means model, while parameter m′ refers to the moderation effect in the means. Subscripts refer to young (y) or old (o) and males (m) or females (f), respectively
