Figure 3. Expression pattern of Gm114 in the embryonic and adult testis suggests that Gm114 might be involved in male germ cell development.
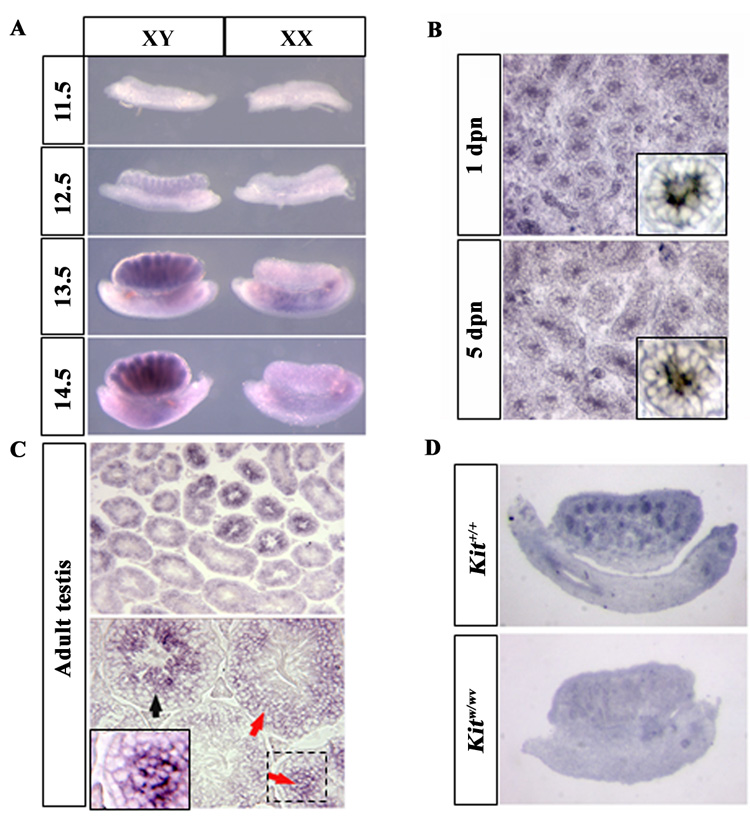
Expression of Gm114 was examined by mRNA in situ hybridization. (A) In the fetal gonad, expression of Gm114 is observed within testis cords and gradually increases between 12.5 and 14.5 dpc, when germ cells are arrested in mitosis and differentiate as prospermatogonia. Expression of Gm114 in germ cells is maintained during postnatal stages, as shown at day 1 and day 5 stages in (B, high magnification of a single cord shown in box). (C) In the adult testis, Gm114 is expressed in germ cells and expression increases throughout germ cell differentiation, with expression in spermatocytes and round spermatids (red arrows and high magnification of boxed region) and the highest expression in elongating spermatids (black arrow). (D) Gm114 expression was low or absent in testes cords of Kitw/wv mutant mice where germ cells are nearly completely absent.
