Figure 6. The testes of Gm114−/− mice develop normally and show no obvious difference from wild type littermates.
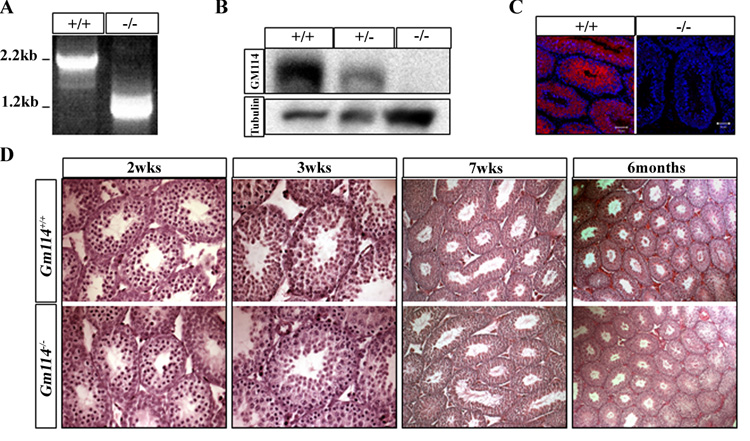
(A–C) GM114 expression is disrupted in mutant testes. Instead of a 2.2kb transcript, the deleted allele produces a 1.2kb transcript shown by RT-PCR (A). 76 kDa GM114 protein was not detected in mutant adult testes by (B) Western blot (γ-tubulin expression is shown as a loading control) or (C) fluorescent immunostaining (GM114 is red and DNA blue (propidium iodide)). The testis of Gm114 −/− mice developed normally and showed no obvious difference from wild type littermates (D). Hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining was performed on mutant and wild type testes at postnatal 2 weeks, 3 weeks, 7 weeks, and 6 months.
