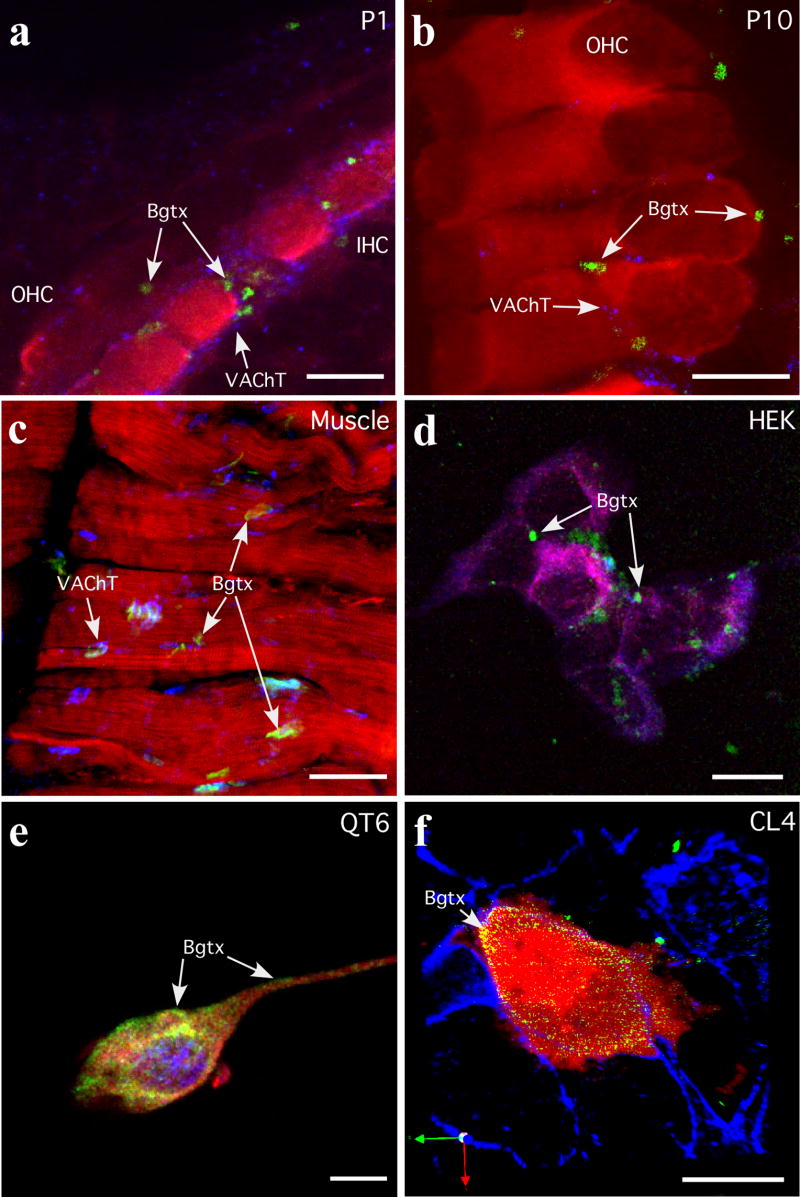
Figure 4.
α-Bungarotoxin (α-Bgtx) labeling of nAChR α9 and α10 in cochlear tissues and cultured cells. (a, b) Cochlear hair cells from P1 and P10 rat pups were labeled with α-Bgtx (488 nm, green), an immunocytochemical hair cell marker, either α-parvalbumin or myosin VI (546 nm, red), and an efferent terminal marker (vesicle acetylcholine transferase, VAChT; 647nm, blue). Arrows identify α-Bgtx labeled clusters. (c) Muscle was used as a labeling control. Shown is muscle diaphragm labeled with α-Bgtx (488 nm, green), phalloidin and myosin VI (546 nm, red), and vesicle acetylcholine transferase (VAChT; 647nm, blue). Arrows identify α-Bgtx labeled neuromuscular junctions. (d) HEK293T cells transfected with nAChR α9, rapsyn and RIC-3 cDNAs were labeled with α-Bgtx (488 nm, green), then processed for immunofluorescence with anti-α9 (594 nm, red), anti-RIC-3 (647 nm, blue). Arrows identify α-Bgtx labeled clusters. (e) QT6 cells transfected with nAChR α9, nAChR α10, and rapsyn cDNAs were labeled with α-Bgtx (488 nm, green), then processed for immunofluorescence with anti-α9 (594 nm, red), anti-rapsyn (647 nm, blue). Arrows identify α-Bgtx labeled regions at the cell surface. (f) CL4 cells transfected with nAChR α9, nAChR α10, rapsyn, and RIC-3 cDNAs were labeled with α-Bgtx (488 nm, green) and then processed for immunofluorescence with anti-GFP (594 nm, red) and phalloidin (647 nm, blue). Arrows identify α-Bgtx labeled regions at the cell surface. The CL4 cell line does not express endogenous α9, α10, rapsyn or RIC-3 as determined by PCR (data not shown), and therefore is a suitable host cell type in which to express functional recombinant α9α10 nAChRs. Scale bars in a,- c frepresent 10 μm and scale bars in d–f represent 20 μm.