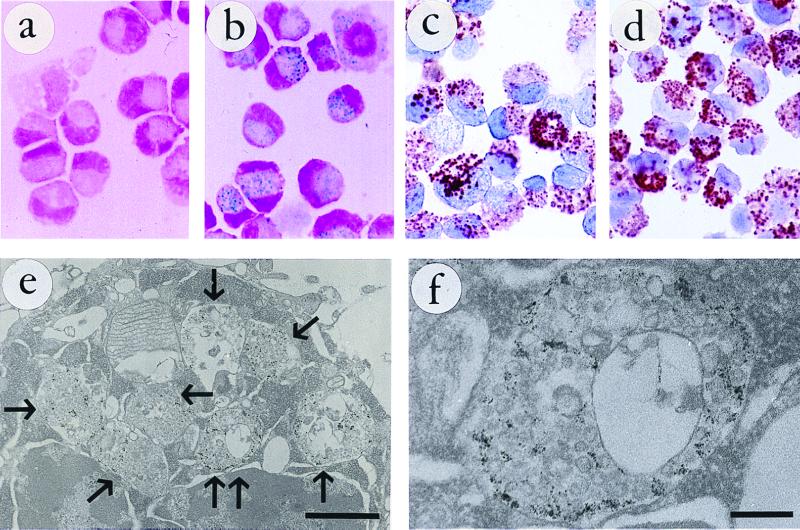
Figure 1.
(a) CG-4 cells labeled for 48 h with 0.5 mg Fe/ml unconjugated MION-46L. No particle uptake can be detected by using the Prussian blue stain for ferric iron. (b–d) CG-4 cells labeled for 48 h with 0.05 mg Fe/ml MION-46L-OX-26. (b) numerous iron-containing vesicles are visible. These vesicles also contain the covalently linked, endocytosed OX-26 mAb, as visualized in c by using immunoperoxidase staining. Under these conditions the total Tfr binding capacity for OX-26 appears nearly saturated, given the similar staining pattern in d by using additional OX-26 mAb added afterward. (e) Transmission electron microscopy of MION-46L-OX-26-tagged CG-4 cells reveals the presence of numerous vesicles (arrows), which measure approximately 0.6–1.0 μm in diameter, and which are filled with the electron-dense magnetic nanoparticles. One of the vesicles (double arrows) is shown at a higher magnification in f to demonstrate the association of particles with a (reversed) endocytosed membrane. All cells in a–f were trypsinized before staining. (Bars represent 1 μm in e and 200 nm in f.)