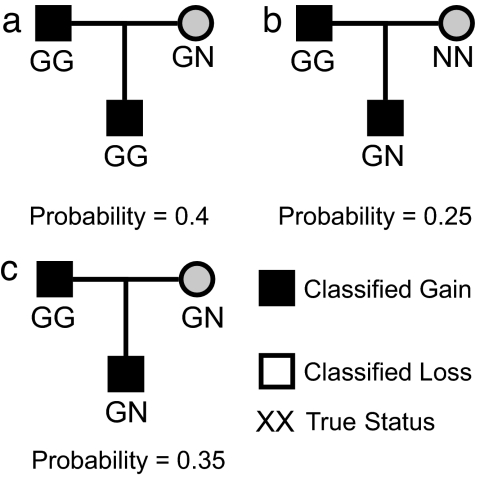
Fig. 2.
A hypothetical example of the final step of the Bayesian reclassification. Illustrated are three plausible true statuses for the situation where the classifications made to father and offspring were “gain” and that to mother was “normal.” If the posterior probabilities associated with each were calculated to be as shown, then methods choosing the most probable family would choose a. We, however, are looking to reclassify the individual and so, for the individuals, sum the probabilities for families that have common states. In this case, the posterior probability that the child is GN is 0.6, and so the posterior statuses assigned would correspond to family (c).