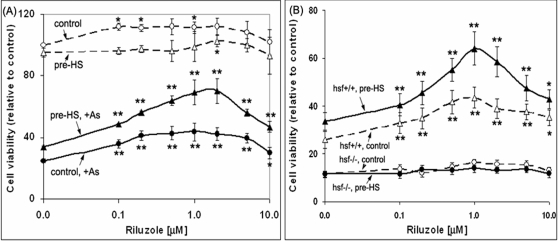
Figure 4. Synergistic effects of riluzle and conditioning heat shock in conferring cell survival under oxidative stress requires a functional HSF1.
(A) Dose response effect of riluzole and conditioning heat shock on cell viability in the absence and presence of oxidative stress challenge. HeLa cells in 96 Strip-well plate were used. The conditions for riluzole treatment and conditioning heat shock were as described in the text. To test for cell survival under conditions of oxidative stress, 20 μM sodium arsenite was added and incubated at 37°C for 24 hr. Viability of the cells was determined using the CellTiter-Glo luminescent reagent from Promega Inc. Cell viability signal, relative to that of the untreated control, is plotted as a function of the concentration of riluzole added. Result represents the average of four independent determinations±standard deviation. * and ** denotes, respectively, two-tailed t-test with a probability of difference between 0.01–0.05 (significant) and <0.01 (highly significant) of the riluzole-treated samples from that of the minus riluzole control. (B) The cytoprotective activity of riluzole and conditioning heat shock requires a functional HSF1 protein. Murine embryo fibroblasts derived from hsf1−/− knockout mice [25] and its hsf1+/+ normal littermate were plated in 96 a Stripwell plate. The conditions used from the treatment of cells with riluzole, conditioning heat shock at 42°C for 2 hr, and assessment of the “cell-kill” effects of arsenite were as described in the text. The figure presents data on viability of the arsenite-challenged cells pretreated with various concentrations of riluzole, without and with conditioning heat shock. Data on viability of the control cells (i.e. without arsenic challenge) are not included in Fig. 4B as they were qualitatively similar to that of the HeLa cells shown in Fig. 4A.