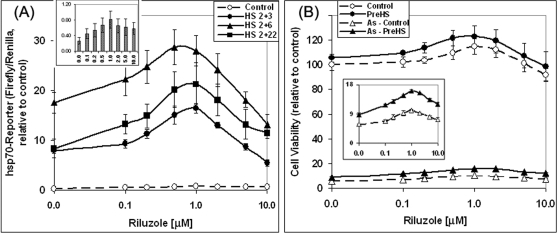
Figure 5. Riluzole amplifies the heat shock response and enhances survival under oxidative challenge in embryonic spinal cord neurons.
(A) Dose-response effect of riluzole on the basal and heat-induced hsp70-luciferase reporter gene in spinal cord neurons. Cells were transfected with the hsp70-firefly luciferase and Renilla luciferase DNA at 10 days in vitro (DIV), a time when the neurons were fully differentiated with a meshwork of processes. Cells in 96 well plates were treated with specified concentrations of riluzole at 37°C for 16 hr. Cells were then heat shocked at 42°C for 2 hr followed by recovery at 37°C for 3, 6 and 22 hr. Cells were harvested and processed for reporter gene assay according to methods described in the text. Result represents the average of four independent determinations±standard deviation. The insert shows an expanded scale of reporter gene activity to better illustrate the effect of riluzole on the basal level (37°C) of reporter gene expression. (B) Synergistic effects of riluzole and conditioning heat shock to enhance survival of spinal cord neurons under oxidative challenge. The conditions of riluzole treatment, heat shock, and arsenite-challenge were as described in the text (same as protocol used in the experiment shown in Fig. 4A for NG108-15 cells). Viability of the cells was determined using the CellTiter-Glo luminescent reagent from Promega Inc. Cell viability signal, relative to that of the untreated control (line 1; without riluzole, 100%), is plotted as a function of the concentration of riluzole added. The insert is an expanded scale to better illustrate the fraction of cells that survived the arsenite-induced oxidative challenge. Result represents the average of four independent determinations±standard deviation.