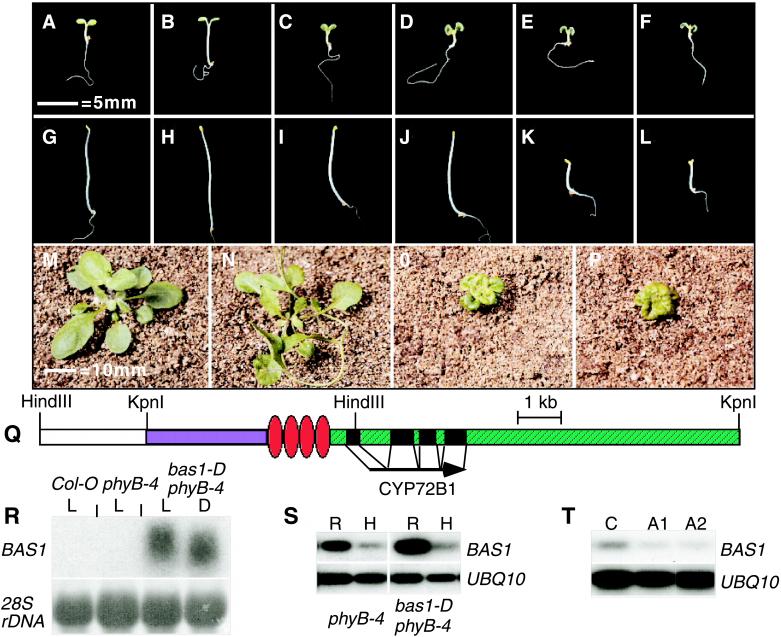
Figure 1.
bas1-D suppresses phyB-4 by the enhanced expression of CYP72B1. (A–F) Six-day-old, light-grown seedlings. (G–L) Dark-grown seedlings: Col-0 (A and G), phyB-4 (B and H), bas1-D phyB-4 (C and I), phyB-4 transformed with the bas1-D gene (D and J), phyB-4 transformed with the CaMV35S∷BAS1cDNA (E and K), and det2–1 (F and L). (M–P) Four-week-old plants: Col-0 (M), phyB-4 (N), bas1-D phyB-4 (O), and det2–1 (P). (Q) A diagram of the insertion, the cDNA, and restriction endonuclease sites used for plasmid rescue. White, part of the antibiotic resistance gene. Blue, pBlueScript sequence. Red, the enhancers. Green, genomic DNA. (R) Northern blot analysis of total RNA from light-grown (L) or dark-grown (D) seedlings. (S) RT-PCR analysis of rosette (R) and hypocotyl (H) tissue. (T) RT-PCR analysis of Col-0 (C) and two bas1 antisense lines (A1 and A2).