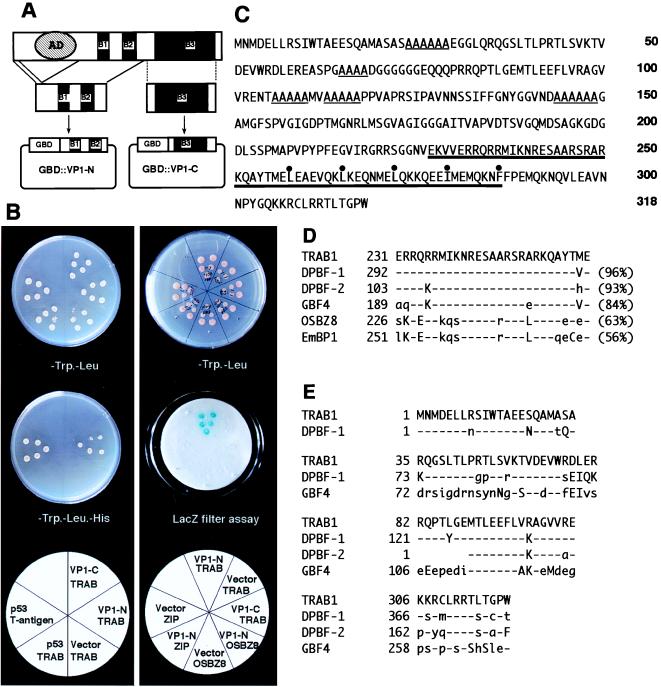
Figure 1.
Isolation and characterization of TRAB1 cDNA. (A) Schematic illustration of the bait construct (pGBD∷VP1-N) used for yeast two-hybrid screening. pGBD∷VP1-C was used as a control bait. The conserved basic regions (B1, B2, and B3) and the acidic transcriptional activation domain of OSVP1 are indicated by solid boxes and a hatched oval, respectively. (B) Yeast two-hybrid assays showing that TRAB1 specifically interacts with the VP1-N fragment. (Left) HIS3 assays. Five independent yeast transformants harboring various combinations of a bait (GBD fusion) and prey (GAD fusion) plasmids were grown on an SD medium plate containing 30 mM 3-aminotriazole, lacking Trp and Leu (Top) or lacking Trp, Leu, and His (Middle). At the bottom, the combination of bait (top line) and prey (bottom line) fragments fused to GBD and GAD, respectively, is indicated in each sector. The combination of the T antigen prey and p53 bait was used as a control for positive interaction. “Vector” indicates a negative control bait of GBD alone (pGBT9). Note that only transformants with the combination of pGBD∷VP1-N and pGAD∷TRAB1 or the positive controls grew on the minus His medium. (Right) LacZ assays. Yeast transformants harboring the indicated combinations of plasmids were grown on an SD medium plate lacking Trp and Leu (Top), and replicate filters were used for LacZ filter assays with X-Gal (Middle). OSBZ8 (12) and ZIP are negative control preys. The cDNA for ZIP was obtained by a yeast one-hybrid screen of the same cDNA library by using the 55-bp ABRC of Osem promoter as a target site and found to encode a protein with a bZIP structure very similar to that of TRAB1 in-frame with GAD. Note that positive signals were obtained only with the combination of GBD∷VP1-N and GAD∷TRAB1. (C) Amino acid sequence of TRAB1 deduced from the nucleotide sequence of the cDNA. The bZIP region and short stretches of Ala residues are indicated by thick and thin underlines, respectively. Hydrophobic amino acid residues that constitute a leucine zipper structure are marked with dots. (D) Comparison between the sequence of the basic region of TRAB1 and those of DPBF-1, DPBF-2, GBF4, OSBZ8, and EmBP1. Percentages of identical amino acids to those of TRAB1 are shown in parentheses. Amino acids identical, similar, and dissimilar to those of TRAB1 are indicated by dashes and uppercase and lowercase letters, respectively. (E) Amino acid sequence blocks conserved between TRAB1, DPBF-1, DPBF-2, and GBF4. Amino acids identical, similar, and dissimilar to those of TRAB1 are indicated by dashes and uppercase and lowercase letters, respectively.