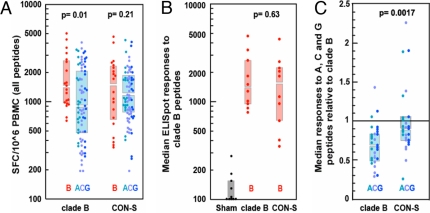
Fig. 3.
Magnitude of each vaccinated monkey's cellular immune responses to clade B envelope and to each of the envelope peptide pools. (A) IFN-γ ELISpot responses of individual monkeys to the 10 envelope peptide series. Each animal's responses to each peptide series are shown in different colored bullets: clade A (aqua), clade C (blue), and clade G (purple). For both cohorts, responses to clade B peptide series are shown in red bullets in separate box plots to facilitate the comparisons of within-clade and between-clade responses. The boxes indicate the IR, and the gap between the two boxes represents the median. The clade B-immunized monkeys had significantly higher clade B peptide-specific responses than non-clade B peptide pools (Wilcoxon rank sum test, P = 0.01). The CON-S-immunized monkeys had statistically indistinguishable responses to clade B and non-clade B peptides. (B) Magnitudes of responses to clade B peptide series are indistinguishable in the two groups of vaccinated monkeys. The median ELISpot responses to the peptide pools for the two clade B peptide series are shown in red bullets, with the median and IR indicated by the boxes. The responses by the control vaccinees are also shown. (C) Median responses to non-clade B peptides relative to clade B peptides in the two groups of vaccinated monkeys. To simplify the visual representation of the data, the PBMC responses of each monkey to the clade A, C, and G peptide series were normalized by dividing those values by the same animal's median clade B-specific PBMC response. Therefore, if an animal had comparable responses to both clade B and non-clade B peptides, a value near 1 would be achieved. The CON-S-vaccinated monkeys had greater magnitude pooled peptide ELISpot responses than the clade B-vaccinated monkeys to the non-clade B envelope peptide pools (Wilcoxon rank sum test, P < 0.0017). The full dataset was used for the plot and the statistics in A to provide a comprehensive view of the data. The median responses to the peptide sets from each clade were used for each animal for B and C to provide an alternative and more conservative view of the results, thereby providing a framework for a statistical comparison in which each animal is counted only once. Because two A, two B, four C, and two G pooled peptide sets were used per animal, the counts in A are not fully independent.