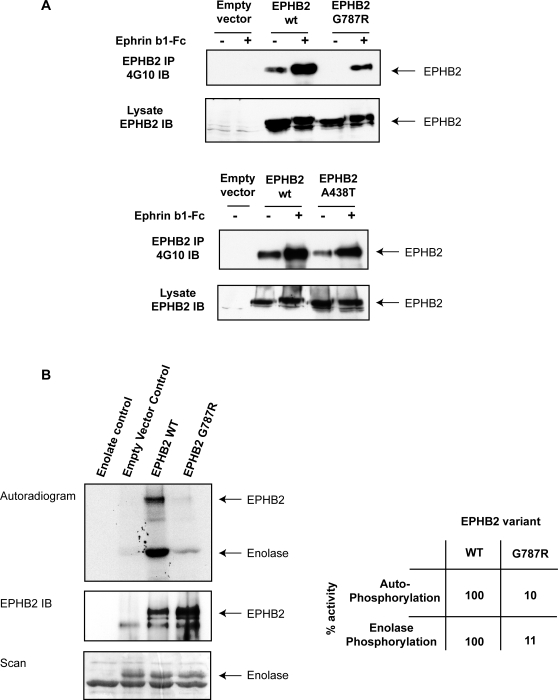
Figure 3. Biochemical characterization of EPHB2 variants.
Panel A: Diminished autophosphorylation of EPHB2 G787R variant in response to ephrinB1 stimulation. DU145 cells were transiently transfected with cDNA constructs (empty vector; wild-type, wt; A438T; G787R) and either left unstimulated (−) or stimulated (+) with preclustered ephrinB1-Fc for 30 min. EPHB2 was immunoprecipitated (IP) and immunoblotted (IB) with antiphosphotyrosine (4G10) to evaluate receptor autophosphorylation. The cell lysate was immunoblotted with antiEPHB2 to ascertain that there was equal transfection efficiency. Panel B: Abolished kinase activity of EPHB2 G787R variant. In vitro kinase assays were performed using wild-type EPHB2 or G787R immunoprecipitates and enolase as the exogenous substrate. Prior to imaging or immonoblotting against EPHB2, phosphorylated proteins were separated by gel electrophoresis and stained with coomassie. Autoradiogram showing 32PγATP incorporation in EPHB2 and enolase (upper panel), anti-EPHB2 immunoblot (middle panel) and equal loading of enolase is shown (lower panel). The table shows the relative kinase activity of the wild-type EPHB2 receptor (set to 100%) vs. the G787R variant.