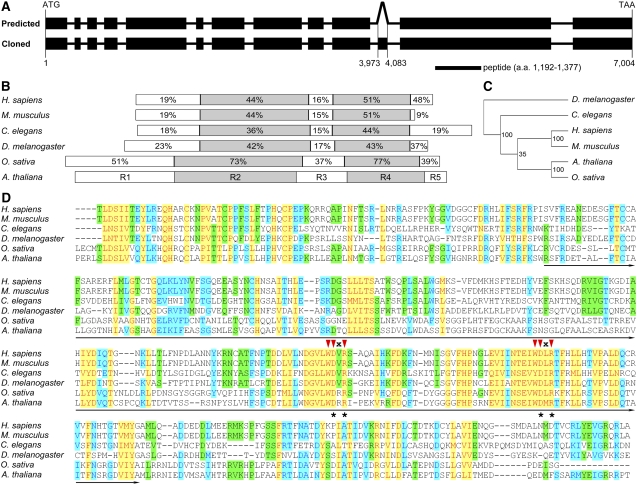
Figure 1.
Structure of the Arabidopsis DCAF1 Gene and Sequence Alignment of DCAF1 Homologs.
(A) Structure of the Arabidopsis DCAF1 gene and the location of the antigen used for antibody preparation. Exons are presented as filled black rectangles, and introns are presented as solid lines. The top diagram (predicted) depicts the predicted structure of the DCAF1 gene in the AGI database with 11 introns and 12 exons. The bottom one (cloned) presents the structure of the DCAF1 gene cloned in this study, which has an extra exon inside the predicted 10th intron, corresponding to nucleotide 3973 to 4083 of the genomic fragment. The position of the peptide used as antigen for antibody preparation is indicated underneath the gene structure. a.a., amino acids.
(B) Schematic comparison of DCAF1 homologs from representative eukaryotic organisms as labeled on the left. Based on the difference in amino acid sequence homology, the DCAF1 proteins are divided into five regions, which, in Arabidopsis, are shown by five differently colored rectangles labeled R1 through R5. The percentages of similarity in the corresponding regions from each homolog to the Arabidopsis DCAF1 are indicated in the respective region.
(C) A phylogenetic tree of DCAF1 homologs from the model organisms indicated on the right (see Methods for details on tree generation procedure). The numbers indicate the statistic values of the reliability for each node.
(D) Alignment of the R4 region of DCAF1 from the model organisms labeled on the left. The WD40 domain is underlined. The red triangles indicate the two WDxR motifs in the WD40 domain, and “x” stands for an indefinite amino acid. The asterisks indicate the Asn and Arg (on the top) within the WDxR motif, which are mutated into the Ala residue in the point mutation analysis as shown in Figure 3A. The shading mode indicates the level of conservation, with red letters in yellow shading corresponding to a high level of conservation (100%), blue letters in azure shading corresponding to a moderate level of conservation (80%), and black letters in green shading corresponding to a low level of conservation (60%).