Fig. 1.
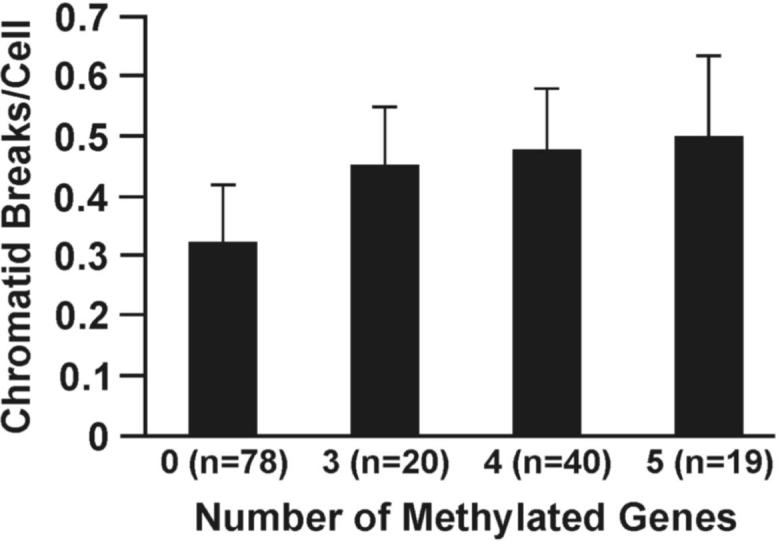
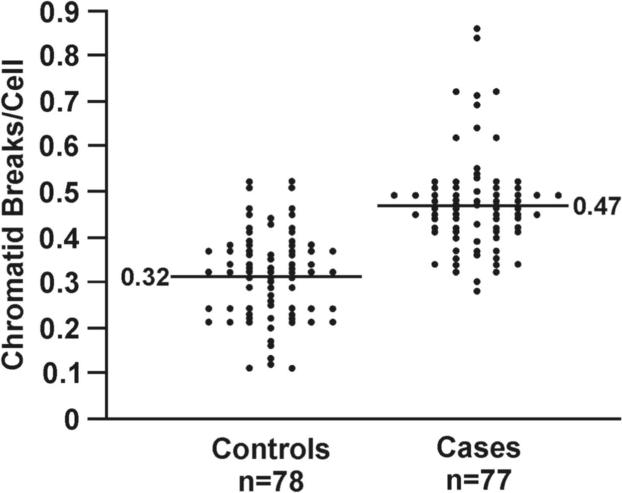
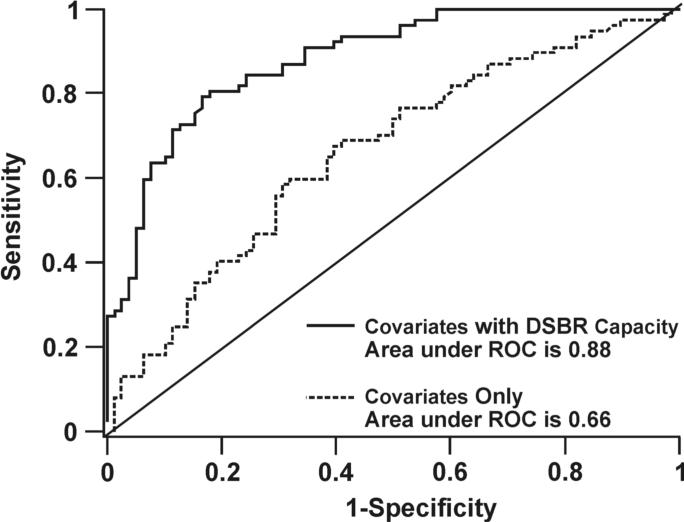
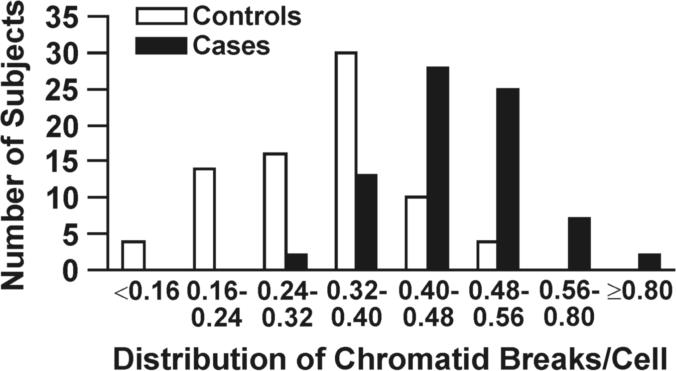
DNA repair capacity is associated with gene promoter methylation in sputum. (A) Bleomycin treatment causes an increased number of chromatid breaks/cell in lymphocytes from cases (methylated group) compared to controls (unmethylated group; p < 0.0001). (B) Positive association between number of methylated genes and chromatid breaks/cell. Sample size for each group is indicated in parentheses. (C) ROC curve comparing sensitivity and specificity of DNA repair capacity for classifying cases and controls. The covariates included in the ROC curve were age at sputum collection, sex, race, current smoking status, and pack years. (D) The distribution of chromatid breaks/cell by case-control status is depicted.