Figure 7. Differential MAPKs regulation by Mst1 cleavage size in DU-145.
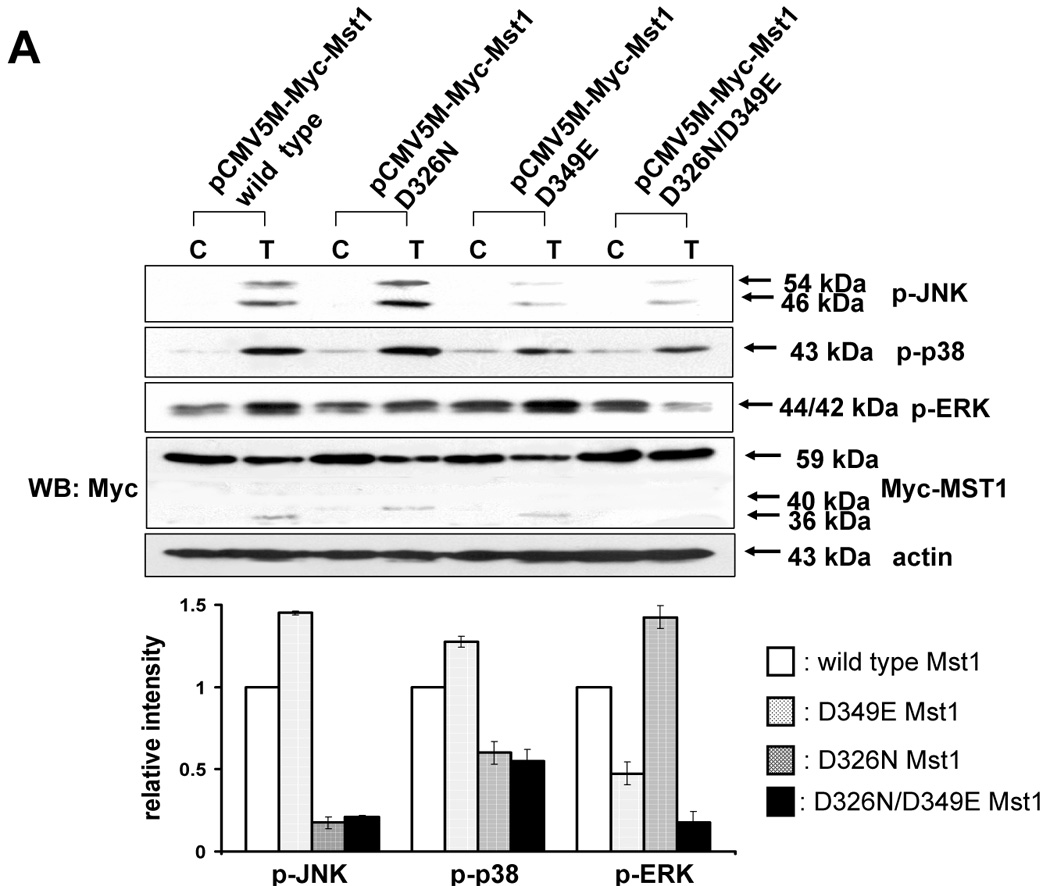
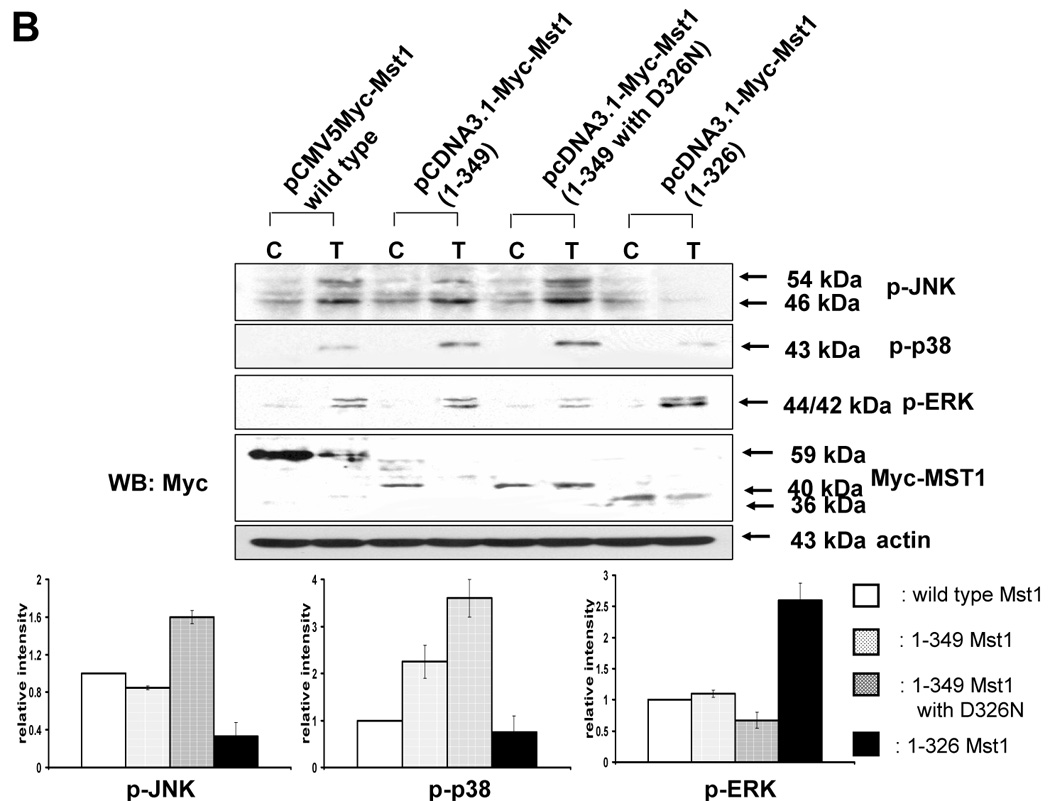
(A) MAPKs phosphorylation was examined after transfection of various mutants of Mst1 in which D326, D349, and both D326 and D349 were mutated. Each construct was transfected into Mst1-knockdown selected cell clone (#6), then after 48 h of transfection, phosphorylation of various MAPKs was examined after the cells were treated with TRAIL (200 ng/ml, 4 h). Upper panel: Western blot analysis, C, control; T, TRAIL. Lower panel: The ratio of the phosphorylated MAPKs to corresponding actin in TRAIL-treated cells was set equal to 1 in wild-type, and the ratio of the phosphorylated MAPKs to corresponding actin in TRAIL-treated cells with different Mst1 deletions was compared to this. Data are expressed as mean ± SE of the densitometry data from three independent experiments. (B) After construction of several deletion mutants of Myc-tagged Mst1 (Myc-tagged 1–349 amino acids of Mst1, Myc-tagged 1–349 amino acids with D326N of Mst1, and Myc-tagged 1–326 amino acids of Mst1), each deletion mutant was transfected into Mst1-knockdown selected cell clone (#6). After 48 h of transfection, phosphorylation of various MAPKs was examined after the cells were treated with TRAIL (200 ng/ml, 4 h). Upper panel: Western blot analysis, C, control; T, TRAIL. Lower panel: The ratio of the phosphorylated MAPKs to corresponding actin in TRAIL-treated cells in wild-type was set equal to 1, and the ratio of the phosphorylated MAPKs to corresponding actin in TRAIL-treated cells with different Myc-tagged Mst1 deletions was compared to this. Note the difference in vertical scale of the three sub-panels. Data are expressed as mean ± SE of the densitometry data from three independent experiments.
