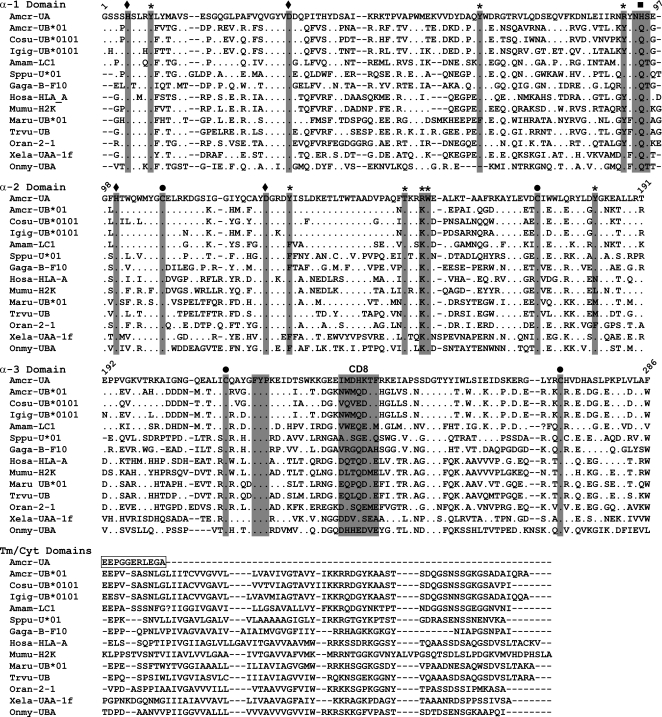
Figure 3. Amino acid alignment of Amcr-UA with other vertebrate class I sequences.
Coding domains are separated according to Koller and Orr [52] and exon/intron information from the Amcr-UA genomic sequence. Numerical labels in the alignment refer to amino acid positions in the Amcr-UA sequence, not in the alignment itself. Shaded columns indicate amino acid positions that are conserved or have expected functions. These amino acid positions also contain the following additional labels: “asterisks” = conserved peptide-binding residues of antigen N- and C- termini; “diamonds” = salt bridge-forming residues; “circles” = disulfide bridge-forming cysteines; “squares” = N-glycosylation site; “CD8” = expected CD8 binding site. The boxed sequence from Amcr-UA represents the 11 amino acid extension that is encoded in exon 4, which corresponds to the α-3 domain. Information and accession numbers of other vertebrate class I sequences can be found in the methods section.