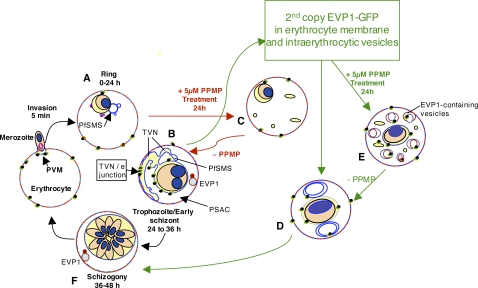
Figure 7. Proposed model for involvement of erythrocyte and parasite rafts, sphingolipid synthesis in the PVM-TVN and EVP1.
Rings (A) bud nascent TVN vesicles (blue) that, in the presence of sphingomyelin synthesis, stabilize into tubules (blue) at the trophozoite stage (B). dl-threo-PPMP inhibits sphingomyelin synthesis in the TVN and blocks development of TVN-tubules (C). Expression of EVP1-GFP stimulates large loops (not tubules) in TVN of trophozoites and schizonts (D). Treatment of transgenic cells with dl-threo-PPMP induces many small loops and vesicles in the erythrocyte (E). These vesicles are stained by a membrane impermeable dye applied to the surface of infected erythrocytes that is usually excluded from uptake in PPMP-treated cells. EVP1 localizes to these vesicles within the erythrocyte shown in red in panels B, E and F. We suggest that EVP1 drives vesicular lipid uptake at the infected erythrocyte membrane, and sphingomyelin synthase drives tubule formation and lipid uptake via tubules possibly to increase the efficiency of uptake. PSAC, Parasite surface anion channel (PSAC) for solute import [5]. TVN/erythrocyte (TVN/e) junction used by host raft proteins and lipids use to directly access the TVN.