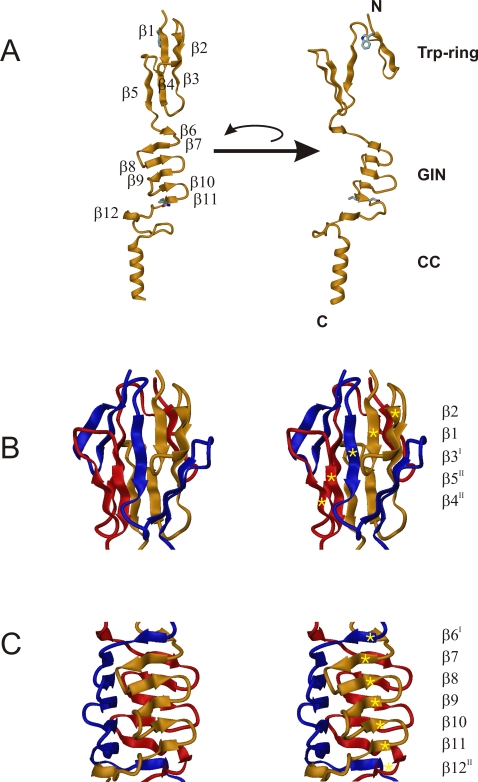
Figure 4. Crystal structure of the BadA head domain.
(A) Structure of the monomeric BadA fragment in ribbon representation with the secondary structure elements marked (β1-β12). Two individual orientations rotated around the threefold axis by 90 degrees relative to each other are shown, and the two domains (Trp-ring domain and GIN domain) and the coiled-coil part (CC) are indicated. The conserved residues Trp387 of the Trp-ring and Gly462-Ile463-Asn464 of the GIN domain which determine their nomenclature are shown in stick representation. (B) Structure of the N-terminal Trp-ring domain in stereo representation. The three independent protein chains are color-coded in yellow, red and blue. The three chains form intertwined mixed parallel/anti-parallel β-sheets, one of which is labeled with gold stars. Its β-strand sequence is β2-β1-β3I-β5II-β4II. (C) Structure of the GIN domain in stereo representation, with the individual monomers color-coded in yellow, red and blue. The three interdigitated chains form three β-sheets, one of which is labeled with gold stars. Its β-strand sequence is β6I-β7-β8-β9-β10-β11-β12II. The strand progression of the individual sheets is anti-parallel (β7-β11) while interacting strands from adjacent chains are combined via parallel strand pairing (β6I-β7 and β11-β12II).