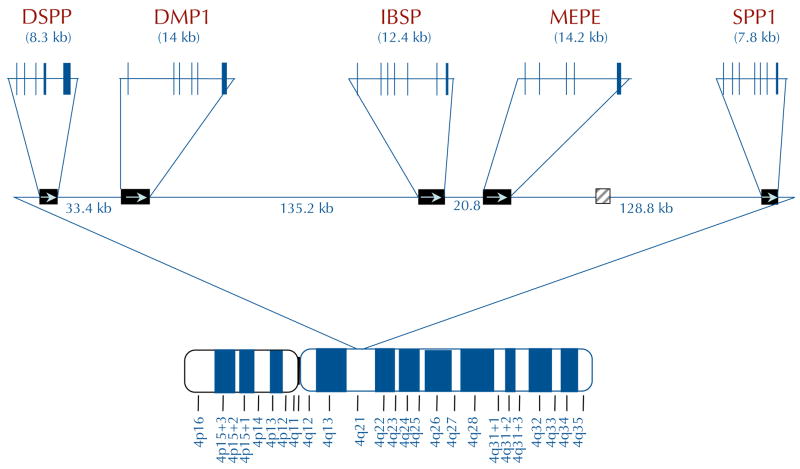
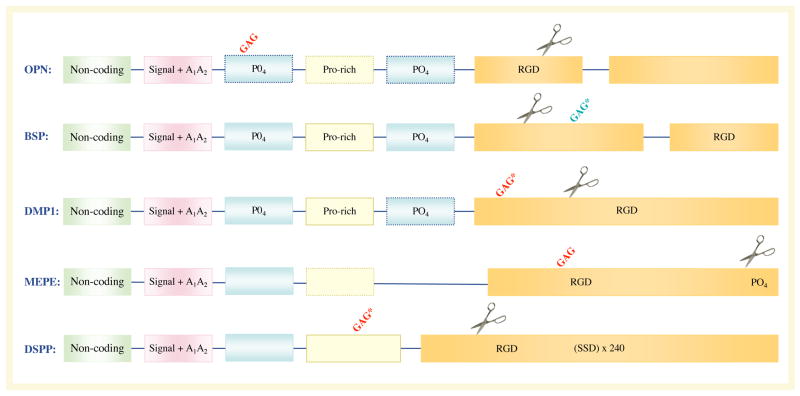
Figure 1. Chromosomal localization and exon–intron similarities of human SIBLInG genes.
a| The genes are clustered within a 375 kb region of chromosome 4 and are similarly arranged in all completed mammalian genomes to date. Except for an apparent pseudogene (HSP90AB177) between matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein (MEPE) and secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1) in humans and chimps only (light grey box), there are no other significant open-reading frames within this region. Integrin-binding sialoprotein (IBSP) encodes bone sialoprotein (BSP) and SPP1 encodes osteopontin (OPN). Vertical lines represent exons. b | The transcripts of small integrin-binding ligand N-linked glycoprotein (SIBLING) genes. The SIBLINGs, which are composed almost exclusively of hydrophilic amino acids, are likely to be flexible, extended structures in solution. The exons (boxes; not drawn to scale) often have similar motifs and properties and are separated by type 0 introns. The first exon is non-coding. The second exon contains the start codon, the hydrophobic signal peptide and the first two amino acids of the mature protein (A1A2). Exons 3 and 5 frequently contain consensus sequences for serine phosphorylation (PO4). Exon 4 can be relatively proline-rich and, like the other small exons (3 and 5), has been shown in some cases to be spliced out of a subset of mRNA (exons with dashed borders). The integrinbinding tripeptide, Arg–Gly–Asp (RGD), is found within the last one or two large exons (which typically encode >80% of the protein). All SIBLINGs contain variously located N- and/or O-linked oligosaccharides, but only the observed (GAG*) and proposed (GAG) consensus attachment sites of the relatively long chain glycosaminoglycans are shown. (Orange GAG indicates chondroitin or dermatan sulphate chains and green GAG indicates keratan sulphate chains.) Cleavage of SIBLINGs (scissors) by specific proteases (bone morphogenetic protein 1 (BMP1), thrombin, matrix metallopeptidases and so on) is thought to be important, although whether this activates and/or inactivates specific SIBLING functions is currently under investigation. Human DSPP also contains ~240 tandem repeats of the phosphorylated nominal Ser–Ser–Asp (SSD) tripeptide. (For summary of some of the post-translational modifications and protease cleavage sites, see REF. 159.) DMP1, dentin matrix protein 1; DSPP, dentin sialophosphoprotein.