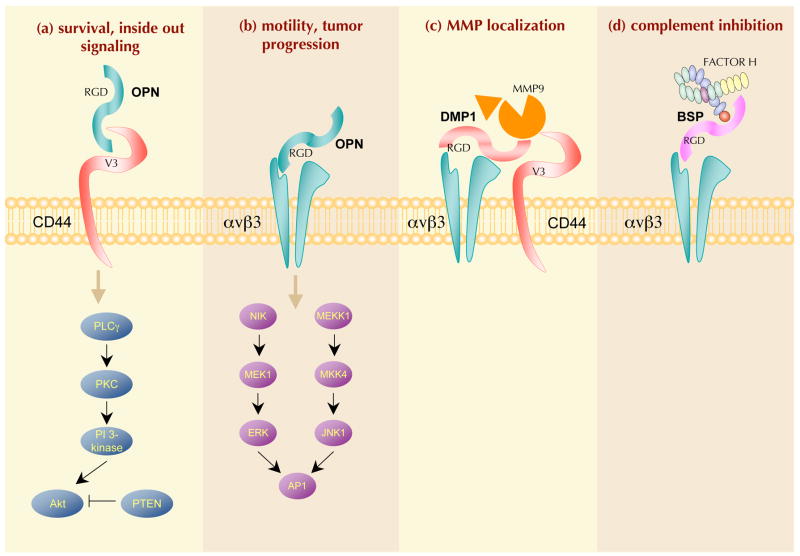
Figure 2. SIBLINGs mediate cell–matrix interactions and cellular signalling.
Small integrin-binding ligand N-linked glycoproteins (SIBLINGs; bone sialoprotein (BSP), dentin matrix protein 1 (DMP1) and osteopontin (OPN) are shown) can initiate Arg–Gly–Asp (RGD)-dependent and RGD-independent interactions with several integrins (such as αvβ3 and a9β1, respectively). OPN (and perhaps DMP1) can also interact with the CD44 family of receptors. Some of these complexes are able to mediate the following functions: (a) cell survival through phospholipase C-γ (PLCγ)–protein kinase C (PKC)–phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)–Akt pathway activation that leads to anti-apoptotic signals in tumour cells. OPN-induced Akt phosphorylation can be blocked by the tumour suppressor PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homologue). However, PTEN is frequently mutated and thus rendered inactive in cancer cells such as melanoma and glioma; (b) motility through the activation of the canonical αvβ3 integrin pathway where both nuclear factorinducing kinase (NIK)–ERK (extracellular signal-related kinase) and MEKK1 (also known as mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1 (MAP3K1)–JNK1 (also known as MAPK8) signalling promote cell migration by activating AP1- dependent gene expression (for a review see REF. 178). Upon binding to αvβ3, OPN also stimulates epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) transactivation, ERK phosphorylation and AP1 activation; (c) bridging of otherwise soluble matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) to cell membranes and their activation, enabling digestion of local extracellular matrix and thereby aiding tissue remodelling and cell migration through the extracellular matrix, a key step for cancer cell invasion; and (d) bridging and activation of complement factor H (CFH) to receptors including αvβ3 integrin. By promoting the degradation of the C3 convertase complex C3bBb, SIBLING-activated CFH disables the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC) and the subsequent lysis of cancer cells, thus favouring their escape from host immune defence. The ? illustrates that it is not known if all binding of SIBLINGs (with or without ligands) necessarily results in signal transduction. MKK4, MAP kinase kinase 4.