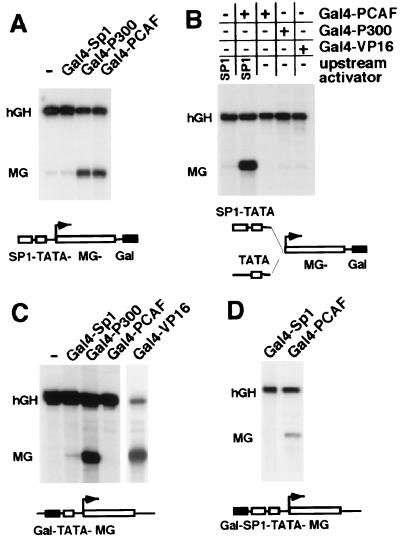
Figure 2.
Direct recruitment of PCAF enhances Sp1-promoter activity similar to the SV40 enhancer. (A) Stimulation of the SP1-TATA-MG-Gal reporter construct by the acetyltransferase PCAF fused to the Gal4-DNA binding domain was compared with the transcriptional enhancement by the known transactivators Gal4-Sp1 and Gal4-p300. The reporter construct SP1-TATA-MG-Gal was transiently transfected with empty vector DNA, Gal4-Sp1, Gal4-p300, or Gal4-PCAF and with the CMV-hGH gene as an internal control for efficiency of transfection. Steady-state RNA levels of the MG fusion genes and the human growth hormone (hGH) gene were determined with the S1-nuclease assay as described in Materials and Methods. (B) The activity of the reporter gene TATA-MG-Gal, lacking upstream-Sp1 binding sites, in the presence of Gal4-VP16, Gal4-p300, and Gal4-PCAF, is shown. For comparison, the stimulation of transcription by Gal4-PCAF in the presence of Sp1 upstream activating sequences is shown in the left two lanes. (C) Gal4-PCAF does not activate transcription by itself. The steady-state levels of the transfected Gal-TATA-MG construct in the presence of Gal4-PCAF were compared with the activity of the reporter gene after cotransfection of empty vector DNA, Gal4-Sp1, Gal4-p300, and Gal4-VP16. The samples derived from cotransfections with different Gal4-fusion proteins were mapped with the same end-labeled probe in the nuclease-S1 assay; however, the Gal4-VP16 derived sample was run on a separate gel. (D) Stimulation by Gal4-PCAF bound at a proximal position, adjacent to the Sp1 upstream activator sites. The reporter gene Gal-SP1-TATA-MG, which contains three copies of Gal4 recognition sites just upstream of multiple Sp1-sites, was cotransfected with Gal4-Sp1 or the Gal4-PCAF expression plasmid.