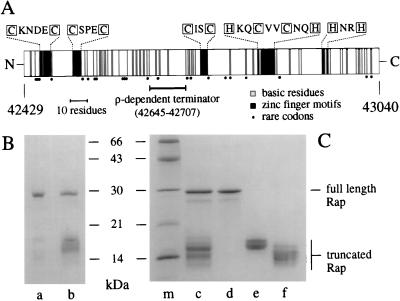
Figure 1.
Structure and purification of λ Rap protein. (A) The rap gene product is represented as a block with N and C termini. Basic residues (arginine and lysine) are indicated by shaded bars. Cysteine and histidine residues (boxed) that may form zinc-finger structures are marked as black bars with the relevant amino acid sequences shown above. Important elements of the gene structure are shown below the protein, namely the predicted location of the ρ-dependent terminator and the position of rare codons. Codons considered rare for E. coli were those with a relative synonymous codon usage of ≤0.04 (30). These codons are CTA (Leu), ATA (Ile), CCC (Pro), AGA, AGG, CGA, CGG (Arg), and GGA (Gly). The nucleotide values given at each end of the figure define the position of rap in the λ genome. (B) Purification of wt Rap. Purified wt Rap protein is in lane a, and His-tag Rap is in lane b. (C) Purification of His-tag Rap proteins by gel filtration. Lane c, Rap proteins eluted from Ni2+ column; lane c, pooled Rap samples separated by gel filtration; lane d, Rap 29K; lane e, Rap 17K; lane f, Rap 14K; and lane m, molecular masses marker proteins (Pharmacia). Proteins were resolved by SDS/PAGE on 13.5% gels and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue.