Abstract
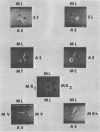
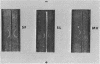
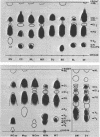
An antiserum to Ca2+-activated adenosine triphosphatase from membranes of Micrococcus lysodeikticus cross-reacted in agar gels with membrane adenosine triphosphatases from other pigmented micrococci and related species. Species of Micrococcus and Sarcina showed different levels of inhibition of adenosine triphosphatase activities in heterologous reactions with antiserum. Inter- and intraspecific relationships based on the inhibition reaction were compared with an independent parameter, namely the quantitative and qualitative composition of the bacterial membrane phospholipids and fatty acids. The guanine plus cytosine contents in the deoxyribonucleic acid of the species studied correlated well with the serological cross-reactivity of adenosine triphosphatases from their membranes. The types of cross-bridges found in the peptidoglycans of these cocci were also compared with the other properties. The results suggest that an antiserum specific for a major membrane protein may be a reliable and most useful adjunct in studying bacterial serotaxonomy.
Full text
PDF


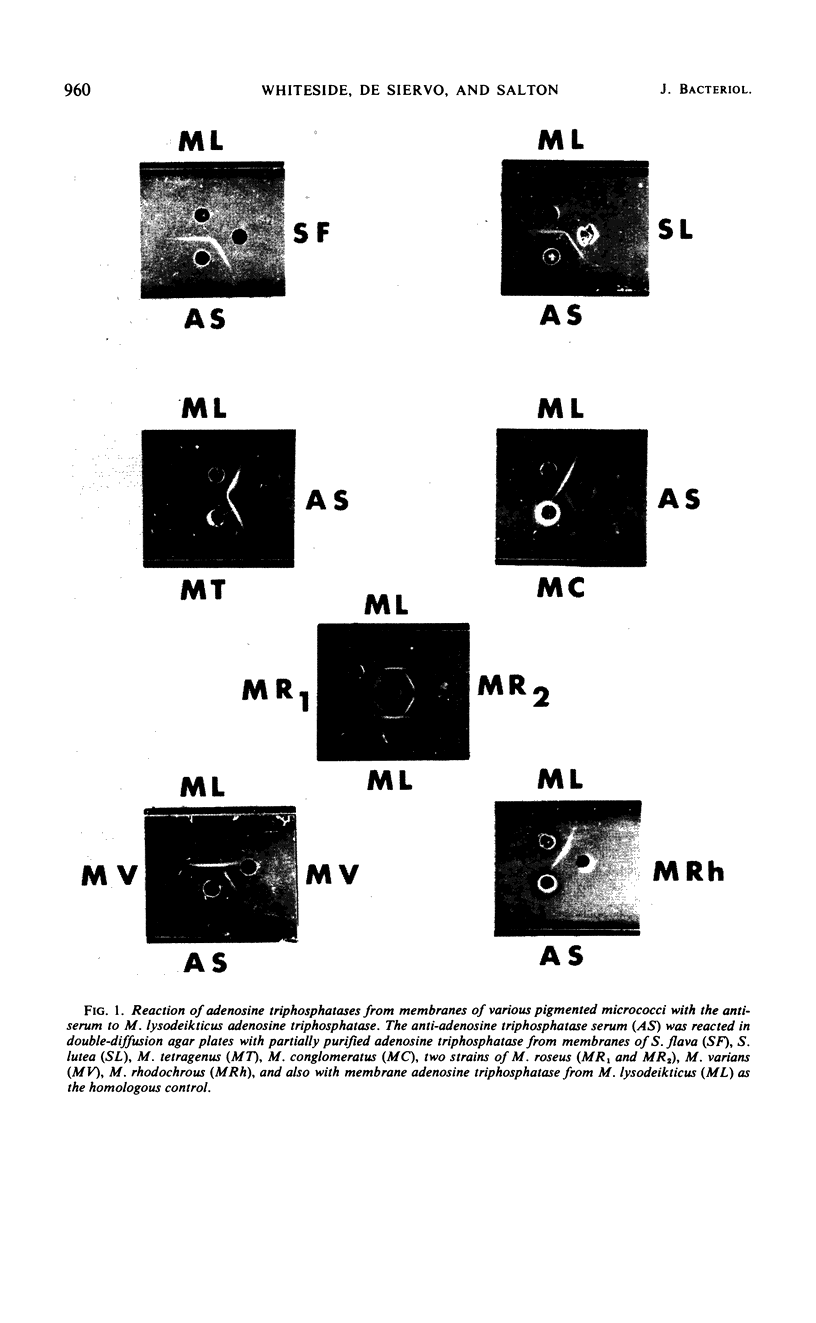
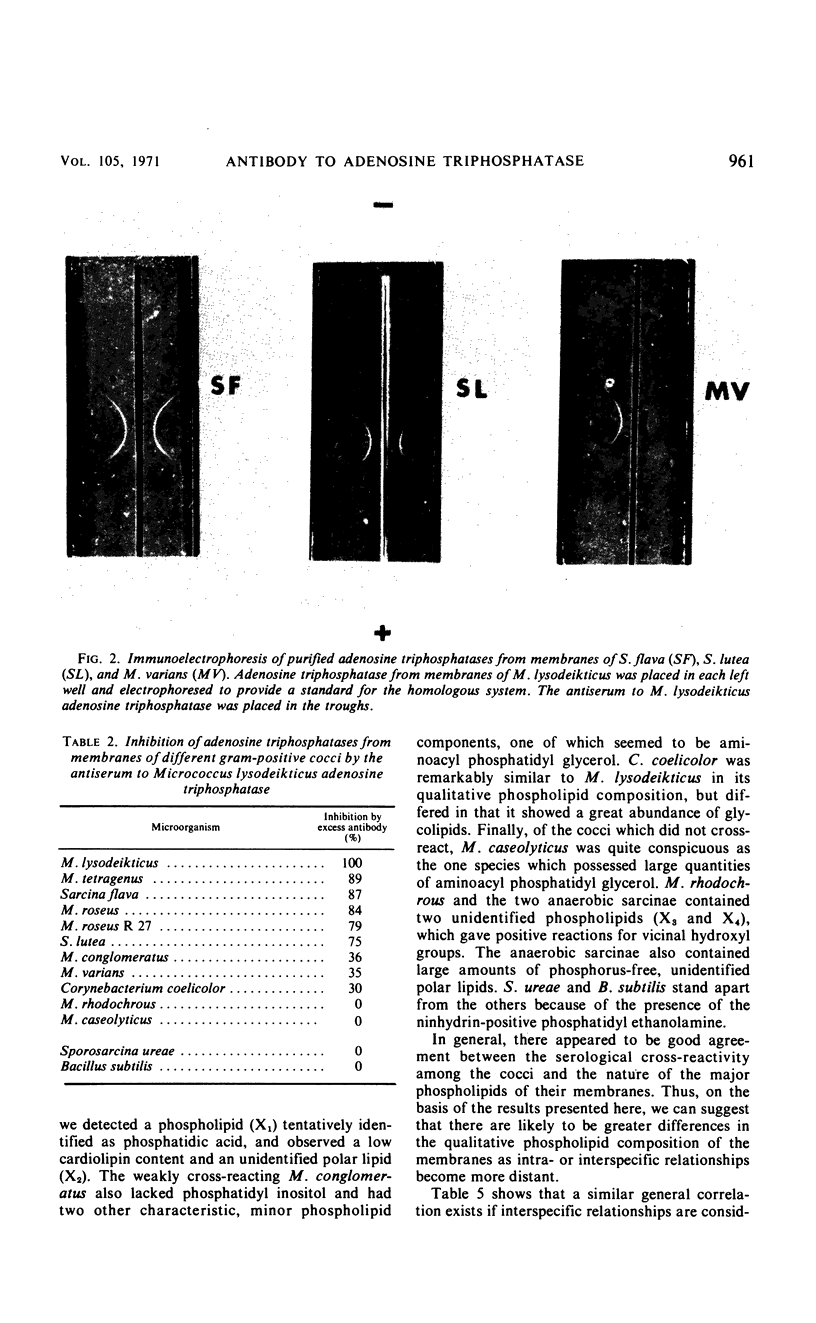
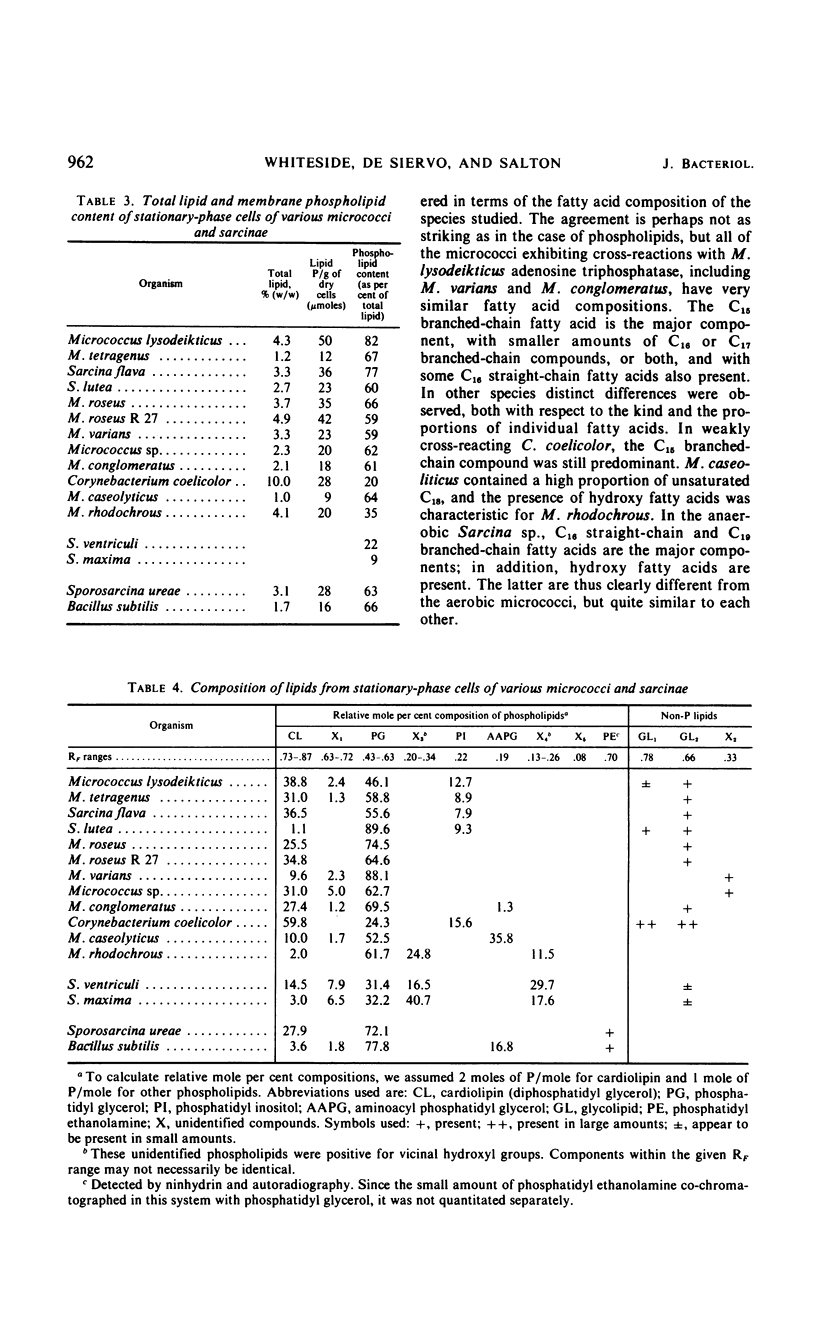
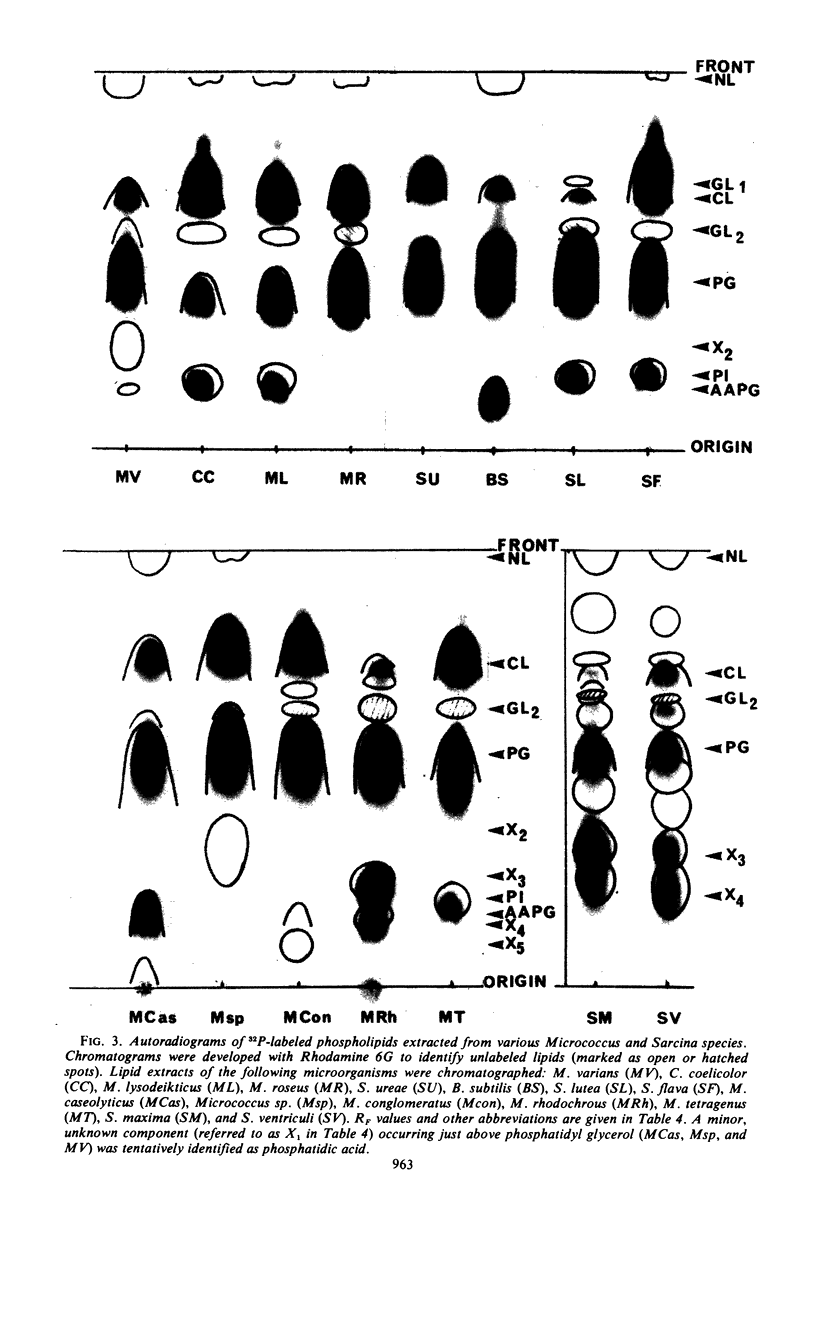



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argaman M., Razin S. Antigenic properties of mycoplasma organisms and membranes. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Jan;55(1):45–58. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auletta A. E., Kennedy E. R. Deoxyribonucleic acid base composition of some members of the Micrococcaceae. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jul;92(1):28–34. doi: 10.1002/path.1700920103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAIRD-PARKER A. C. THE CLASSIFICATION OF STAPHYLOCOCCI AND MICROCOCCI FROM WORLD-WIDE SOURCES. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Mar;38:363–387. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohácek J., Kocur M., Martinec T. Deoxyribonucleic acid base composition of Sporosarcina ureae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;64(1):23–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00412127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canale-Parola E., Mandel M., Kupper D. G. The classification of sarcinae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;58(1):30–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00691165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocks G. T., Wilson A. C. Immunological detection of single amino acid substitutions in alkaline phosphatase. Science. 1969 Apr 11;164(3876):188–189. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3876.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON R. E., MIHM J. M. A comparative study of some strains received as nocardiae. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jan;73(1):15–27. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.1.15-27.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M. Use of bacteriolytic enzymes in determination of wall structure and their role in cell metabolism. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 2):425–464. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Canale-Parola E. Fine structure of Sarcina maxima and Sarcina ventriculi. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):399–410. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.399-410.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E. Transformation of Micrococcus lysodeikticus by various members of the family micrococcaceae. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Dec;59(2):247–255. doi: 10.1099/00221287-59-2-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANEELLE M. A., ASSELINEAU J., CASTELNUOVO G. ETUDES SUR LES MYCOBACT'ERIES ET LES NOCARDIAE. IV. COMPOSITION DES LIPIDES DE MYCOBACTERIUM RHODOCROUS, M. PELLEGRINO SP., ET DE QUELQUES SOUCHES DE NOCARDIAE. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Jan;108:69–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARINETTI G. V. CHROMATOGRAPHY OF LIPIDS ON COMMERCIAL SILICA GEL LOADED FILTER PAPER. J Lipid Res. 1965 Apr;6:315–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazanec K., Kocur M., Martinec T. Electron Microscopy of Ultrathin Sections of Sporosarcina ureae. J Bacteriol. 1965 Sep;90(3):808–816. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.3.808-816.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. M., Mills S. E. Immunochemical and enzymatic comparisons of the tryptophan synthase alpha subunits from five species of Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1310–1320. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1310-1320.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz E., Salton M. R., Ng M. H., Schor M. T. Membrane adenosine triphosphatase of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Purification, properties of the "soluble" enzyme and properties of the membrane-bound enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):490–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosypal S., Rosypalová A., Horejs J. The classification of micrococci and staphylococci based on their DNA base composition and adansonian analysis. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Aug;44(2):281–292. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-2-281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. Amino acid sequence of the murein of Planococcus and other Micrococcaceae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):387–392. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.387-392.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Wachter D., Gasser C., Wilson A. C. Comparative immunological studies of two Pseudomonas enzymes. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):351–362. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.351-362.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornabene T. G., Morrison S. J., Kloos W. E. Aliphatic hydrocarbon contents of various members of the family Micrococcaceae. Lipids. 1970 Nov;5(11):929–937. doi: 10.1007/BF02531125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASSERMAN E., LEVINE L. Quantitative micro-complement fixation and its use in the study of antigenic structure by specific antigen-antibody inhibition. J Immunol. 1961 Sep;87:290–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Frerman F. E. Extraction, characterization, and cellular localization of the lipids of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1854–1867. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1854-1867.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteside T. L., Salton M. R. Antibody to adenosine triphosphatase from membranes of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochemistry. 1970 Jul 21;9(15):3034–3040. doi: 10.1021/bi00817a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuthier R. E. Two-dimensional chromatography on silica gel-loaded paper for the microanalysis of polar lipids. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jul;7(4):544–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]