Figure 7.
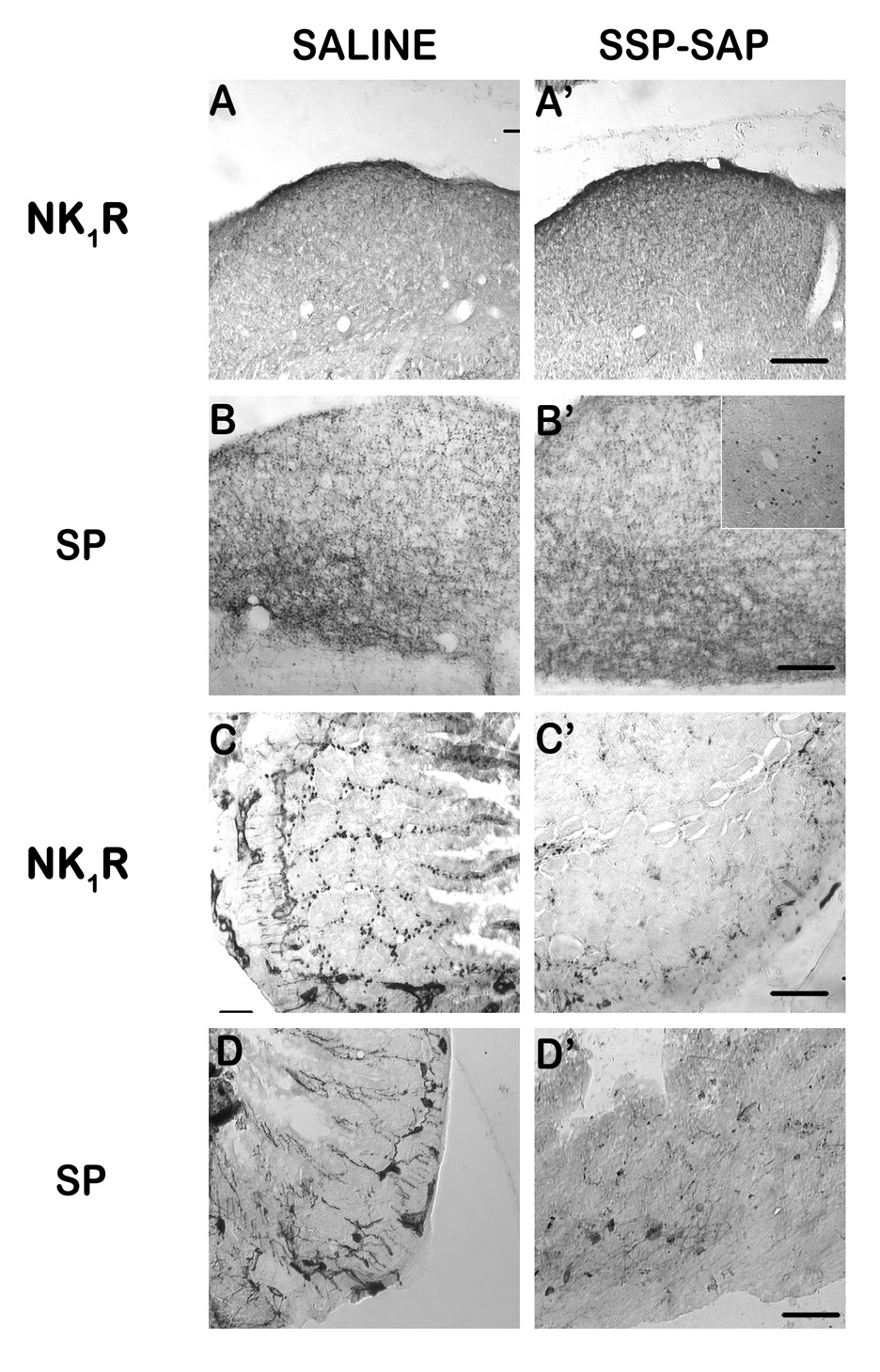
Immunohistochemical analysis of immunotoxin lesion. SSP-SAP (1.2 mg/kg, i.p.) was injected to lesion NK1 receptor-containing cells in the gut. Immunolabeling for NK1 receptors and Substance P (SP) was used to assess the lesion. A–B) Labeling in the dorsal vagal complex (DVC) of saline-(A/B) or SSP-SAP-injected (A’/B’) shrews appeared normal for both NK1 receptor (A/A’) and SP (B/B’). C–D) Relative to saline control (C), labeling in the small intestine showed a distinct and extensive loss of NK1 receptor (C’) containing cell bodies and fibers in the myenteric plexus, crypts, and villi, although the loss was not complete. SP-containing cell bodies in the intestinal nerve plexi were present in both saline (D) and SSP-SAP (D’) treated shrews, but fibers extending into the intestinal villi and crypts appeared to be reduced in number relative to controls. The inset in B’ shows the presence of Fos-IR within the DVC following i.p. injection of GR73632 and vomiting in a SSP-SAP-injected shrew, demonstrating that the NTS is still functionally responsive to emesis. Scale bars (Except inset) = 50 µm.
