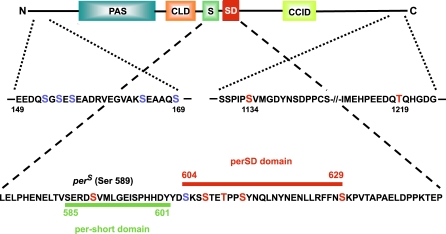
Figure 4. Distribution of Phosphorylated Regions in PER Relative to Functional Domains or Motifs.
Colored blocks show functional domains found in PER. Three regions phosphorylated by DBT are shown as segments of PER protein sequence, with phosphorylated residues established in this study indicated in red. Four serines between aa 143–169, as well as serine 604, are shown in blue, as they are potential targets within DBT-derived phosphopeptides, but could not be directly assessed for phosphorylation in this study; see also the text). PAS indicates position of PAS domain (contains aa ∼220–450) [51]; CLD, cytoplasmic localization domain that promotes PER cytoplasmic localization in the absence of TIM (aa 452–512) [52]; S, per-short domain, causes short-period behavioral rhythms when variably mutated (indicated as a green bar; 585 and 601 indicate the first and last amino acid of the motif, respectively) [24]; SD, per-short downstream domain, contains many DBT phosphorylation sites (indicated by the red bar above the protein sequence; 604 and 629 indicate the first and last amino acids, respectively, of the region examined in this study); CCID, CLK-CYC inhibitory domain, represses CLK-dependent transactivation when overexpressed in cultured cells [39]. (N and C indicate the amino- and carboxy-terminal ends of the schematic PER).