Fig 5. Effect of plasmid-based expression of T1L and T3D μ2 on M1-si-based reduction of infectious viral yields.
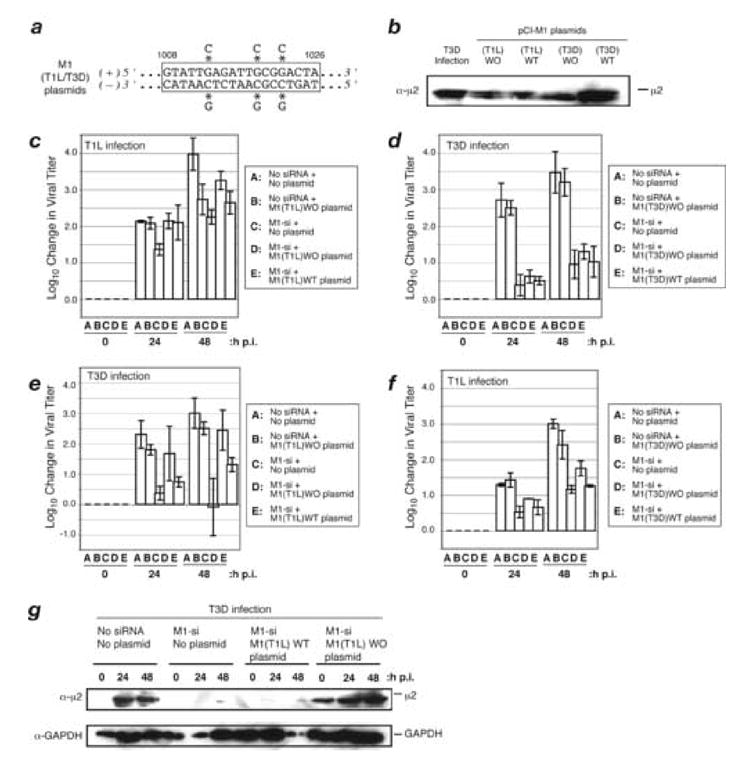
(A) Sequence of rescue plasmid encoding T1L and T3D M1 in the region targeted by M1-si. Asterisks indicate the nucleotides that were changed to encode silent (wobble) mutations. (B) CV-1 cells were transfected with 5 μg of either pCI-M1(T1L) or pCI-M1(T3D) rescue plasmids. In each case, these plasmids either contained wobble mutations in the M1-si-targeted sequence (designated as WO plasmids) or did not (designated as WT plasmids). The cells were incubated for an additional 24 h p.i., and cell-associated proteins were prepared for SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. Protein was detected using specific antibodies against μ2. (C, D, E, F) CV-1 cells were transfected with no siRNA, M1-si, or M1-si in combination with a particular rescue plasmid, and at 24 h p.t. were then infected with T1L (C, F) or T3D (D, E) reovirus at 10 PFU/cell. Cells were harvested at 0, 24, or 48 h p.i., and viral titers were determined by plaque assays. Log10 changes in viral titer relative to time 0 are indicated. Each bar represents the average obtained from three independent experiments, and error bars indicate the standard deviations. (G) CV-1 cells were transfected with no siRNA, M1-si, or M1-si in combination with either M1(T1L)WT or M1(T1L)WO plasmid, and at 24 h p.t. were then infected with T3D reovirus. The cells were incubated for an additional 0, 24, or 48 h p.i., and cell-associated proteins were prepared for SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. Protein was detected using specific antibodies against μ2 or GAPDH.
