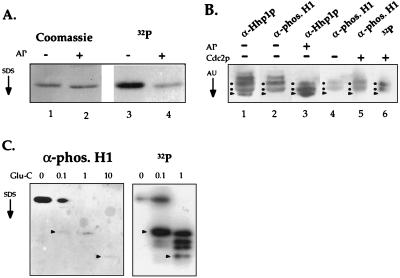
Figure 4.
HHP1p is multiply phosphorylated by using two potential Cdc2 kinase phosphorylation sites. (A) HHP1p is phosphorylated in vivo. Vegetative cells were labeled continuously during growth with 32P-orthophosphate. RP-HPLC-purified HHP1p was treated with AP (+) or buffer only (−), resolved by 12% SDS/PAGE, and analyzed by Coomassie staining and autoradiography. (B) Hhp1p was incubated in the presence (+) or absence (−) of AP. As well, AP-treated Hhp1p was incubated with (+) or without (−) Cdc2 in a standard kinase reaction. All samples were then resolved on a long (30 cm) acid-urea gel and analyzed by autoradiography (where appropriate) or by immunoblotting by using α-Hhp1p or α-phosphorylated H1 antisera. Dots indicate the putative isoforms phosphorylated by Cdc2 kinase, and the arrow heads point to the faster migrating, dephosphorylated isoform. (C) Gel-purified, unlabeled Hhp1p (Left) as well as in vitro-phosphorylated Hhp1p (Right) were partially digested by Glu-C protease, resolved on a 22% SDS/PAGE, and analyzed by immunoblotting by using the phosphorylated H1 antiserum (Left) or autoradiography (Right). Arrow heads point to peptides that are detected in both cases. Reactivity of Hhp1p peptides with the phosphorylated H1 antiserum is reduced after Glu-C digestion for reasons that remain unclear. The amount (in micrograms) of Glu-C used in each reaction is indicated at the top of each lane.