Figure 4.
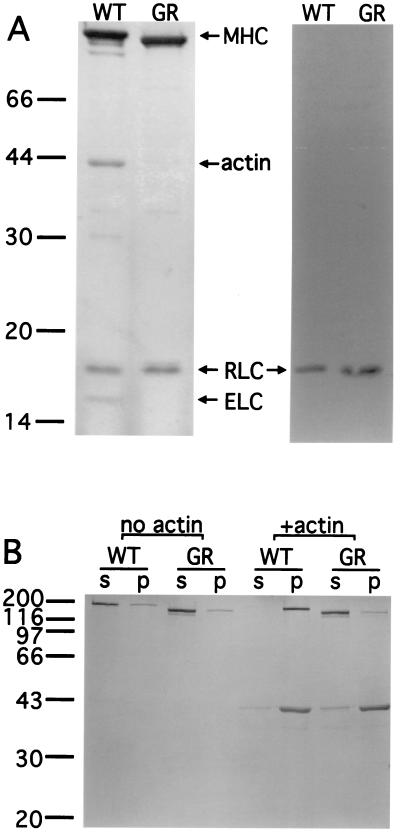
GFP-RLC-myosin rod binds RLC but does not interact with actin. (A) (Left) Wild-type myosin II and GFP-RLC-myosin rod were partially purified from whole cell lysates by two rounds of assembly and disassembly, and the second pellets are shown. Wild-type myosin II (WT) purifies with both light chains bound, whereas the GFP-RLC-myosin rod (GR) purifies only with RLC, as expected. Note that the wild-type myosin II copurifies with a significant amount of actin, which is not the case for the GFP-RLC-myosin rod because it lacks the actin-binding domain. (Right) Western blot probed with anti-RLC antibody confirms the identity of the RLC. (B) Purified wild-type myosin or GFP-RLC-myosin rod at 0.1 mg/ml in a buffer of 10 mM Hepes, pH 7.4/250 mM NaCl/1 mM DTT/5 mM EDTA were incubated for 15 min with or without actin on ice and then centrifuged at 55,000 rpm in a TL100.1 rotor at 4°C. In the absence of actin, most wild-type myosin II or GFP-RLC-myosin rod remained in the supernatant. With the addition of 0.2 mg/ml actin, all wild-type myosin II molecules sedimented into the pellet along with actin filaments. However, GFP-RLC-myosin rod molecules were not affected by the sedimentation of actin filaments; most remained in the supernatant. s, Supernatant; p, pellet.