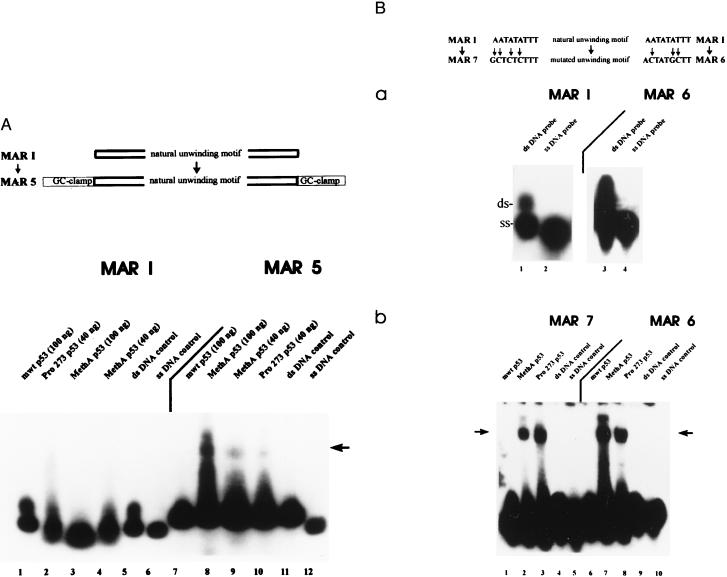
Figure 3.
Influence of sequence context on mutant p53-mediated strand separation of MAR-oligonucleotides. (A) The MAR 5 oligonucleotide was created by the addition of GC-clamps to both ends of the MAR I oligonucleotide, and the interactions of wt and different amounts of mut p53 with the 32P-end-labeled MAR I or MAR 5 probes were compared in EMSA. Reactions with MAR I were carried out in the presence of different amounts of MethA p53 (lane 3, 100 ng; lane 4, 40 ng), human Pro-273 p53 (lane 2, 40 ng), or wt p53 (lane 1, 100 ng). The MAR 5 probe was incubated with wt p53 (lane 7, 100 ng), MethA p53 (lane 8, 100 ng; lane 9, 40 ng), or human Pro-273 p53 (lane 10, 40 ng). Lanes 5 and 11, control reactions with MAR I (lane 5) or MAR 5 (lane 11) in the absence of p53; 6 and 12, aliquot of the ss MAR I and MAR 5 probe. (B) MAR 7 and MAR 6 oligonucleotides were created by inserting mutations into the unwinding motif of MAR I (indicated by arrows) and subjected to EMSA in the absence or presence of wt p53 or mut p53. (a) Aliquots of the isolated ss and ds MAR I and MAR 6 were subjected to EMSA in the absence of p53 to analyze their ability for spontaneous strand separation under EMSA conditions. (b) Binding reactions were performed with 32P-end-labeled MAR 7 probe in the presence of equal amounts (100 ng) of murine wt p53 (lane 1), murine MethA p53 (lane 2), human Pro-273 p53 (lane 3), or in the absence of protein (lane 4). Lane 5, aliquot of the ss MAR 7 probe. The MAR 6 probe was subjected to EMSA with murine wt p53 (lane 6), murine MethA p53 (lane 7), and human Pro-273 p53 (lane 8), or in the absence of p53 (lane 9). Lane 10, aliquot of the ss MAR 6 probe.