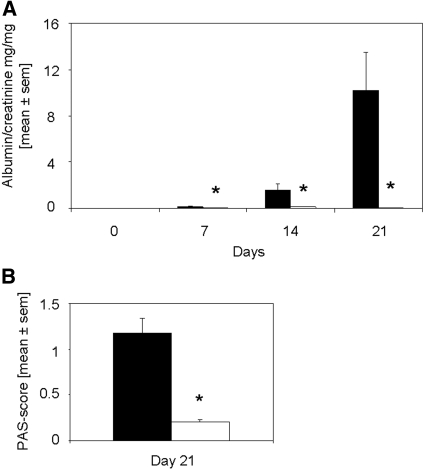
Figure 1.
Rapamycin started on the day of immunization significantly reduces albuminuria and PAS-positive deposits in glomeruli. (A) Albumin and creatinine were evaluated on days 0, 7, 14, and 21 after induction of anti-GBM GN. Urine albumin excretion (in mg) was determined and expressed per mg of urinary creatinine to standardize for the urine concentration. Mice that were treated with rapamycin (□; n = 16 at days 0, 7, and 14; n = 8 at day 21) starting on the day of immunization displayed significantly decreased albuminuria on days 7, 14, and 21 as compared with vehicle-treated mice (▪; n = 14 at days 0, 7, and 14; n = 7 at day 21). *P < 0.05. (B) PAS-positive deposits were scored in glomeruli of rapamycin- (□; n = 8) and vehicle-treated mice (▪; n = 7) on day 21 after induction of disease. The mean score of 50 glomeruli is given. Rapamycin-treated mice displayed significantly decreased PAS-positive deposits. *P < 0.05.