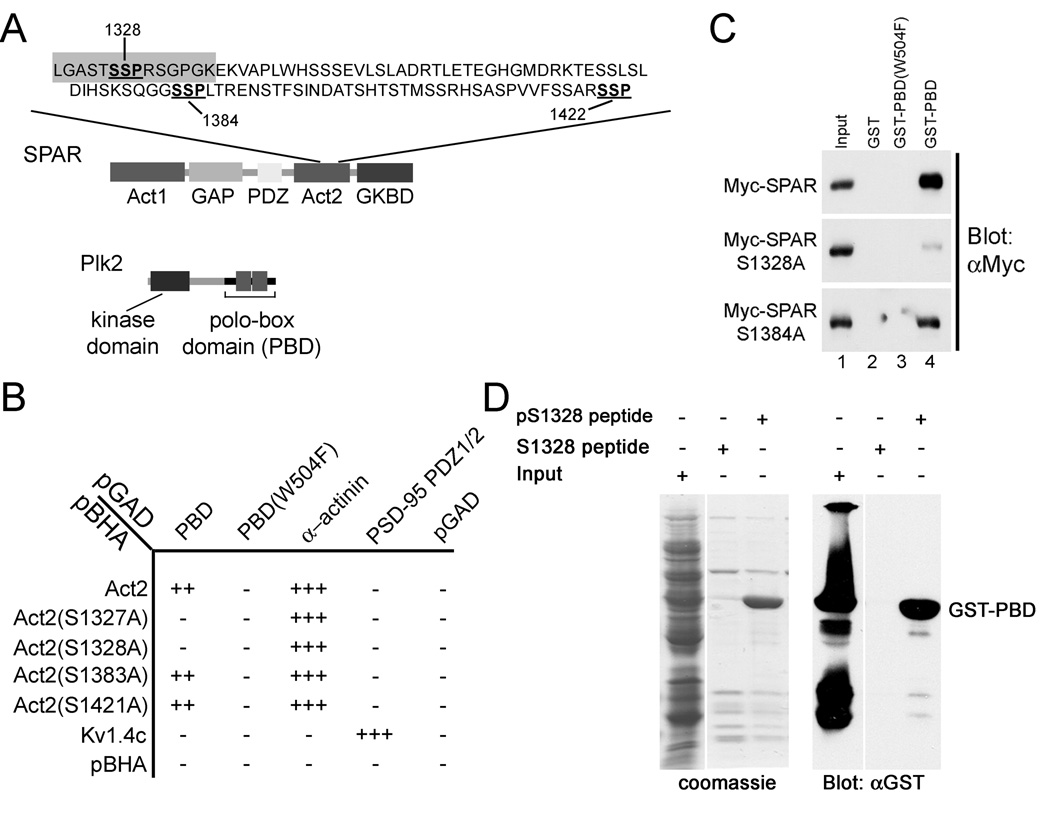
Figure 2. Plk2-PBD binds to canonical PBD binding site in SPAR.
(A) Domain organization of Plk2 and SPAR proteins. Candidate Plk2-PBD binding sites (SSP) within Act2 domain of SPAR are underlined. pS1328 and S1328 peptide sequences used in (D) are highlighted in gray.
(B) Interaction of the Plk2-PBD (PBD) with SPAR-Act2 and Act2 mutants in yeast two-hybrid system. Alpha-actinin, PSD-95, and Kv1.4 are positive controls. pGAD and pBHA are empty vector negative controls.
(C) Glutathione S-transferase (GST)-PBD pull-down of myc-tagged SPAR and myctagged SPAR mutants. Extracts of HEK293 cells transfected with myc-tagged SPAR or indicated SPAR mutants were incubated with Glutathione sepharose beads coupled to GST alone, GST-PBD(W504F), or GST-PBD, as indicated. Bound proteins were immunoblotted for myc. Lane 1 was loaded with 0.5 % of the input.
(D) Binding of GST-PBD to phosphorylated ser-1328 peptide (pS1328). pS1328 and non-phosphorylated S1328 peptides were coupled to agarose beads and incubated with extracts from bacteria expressing GST-PBD. Bound proteins were analyzed by Coomassie blue staining or immunoblotting with GST antibodies. Input lane, 10% of extract loaded onto beads.